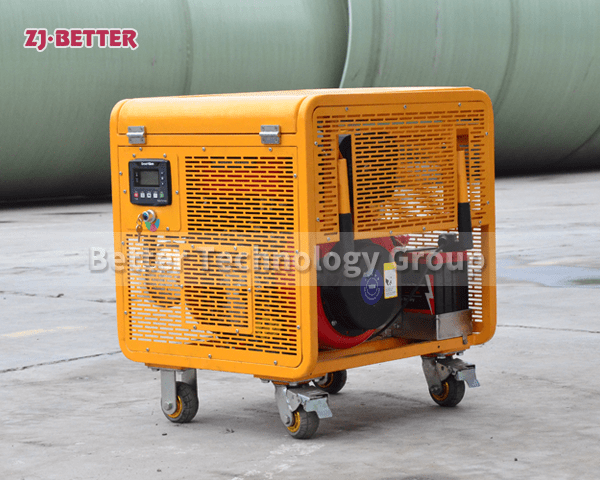
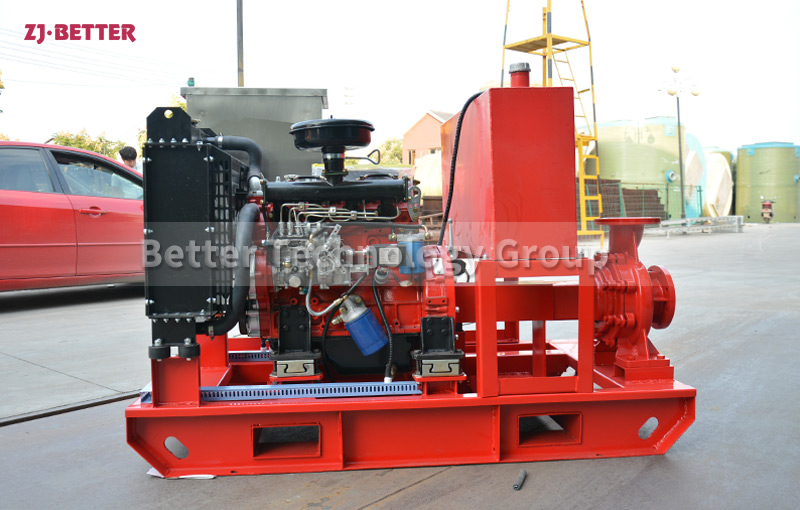
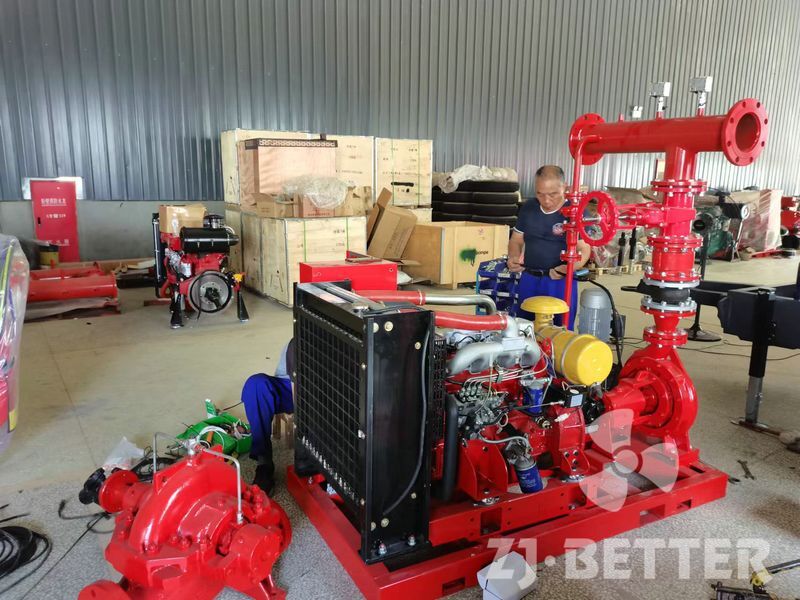
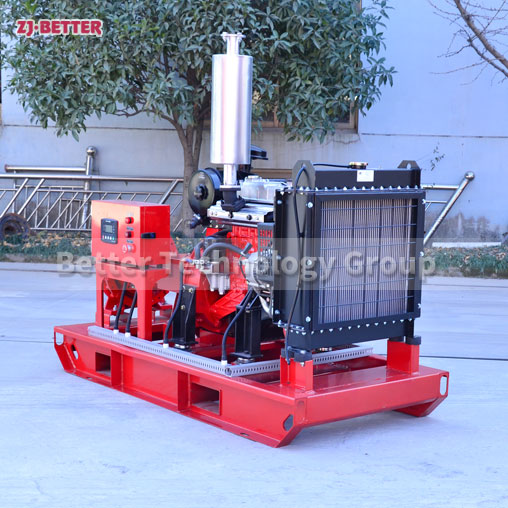
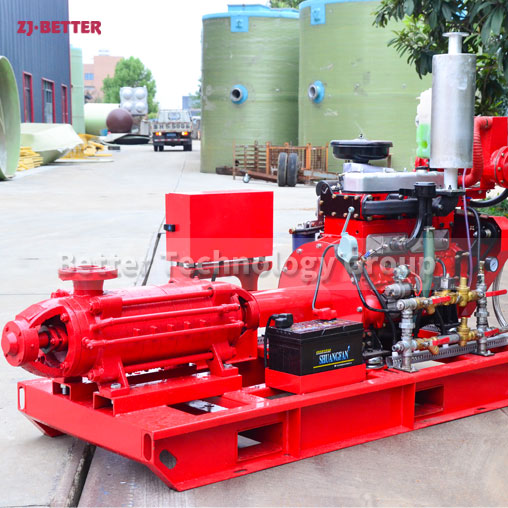
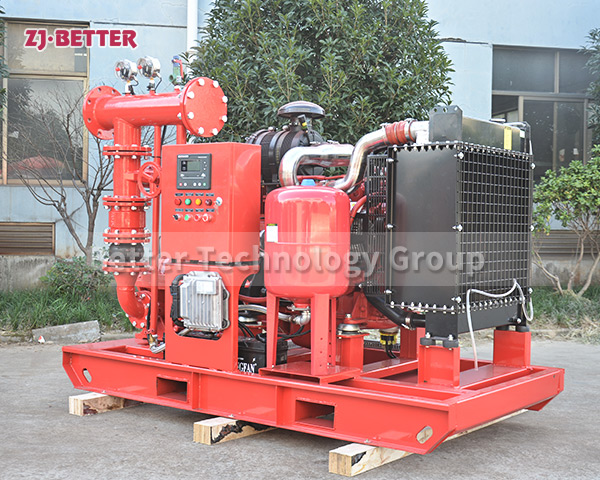
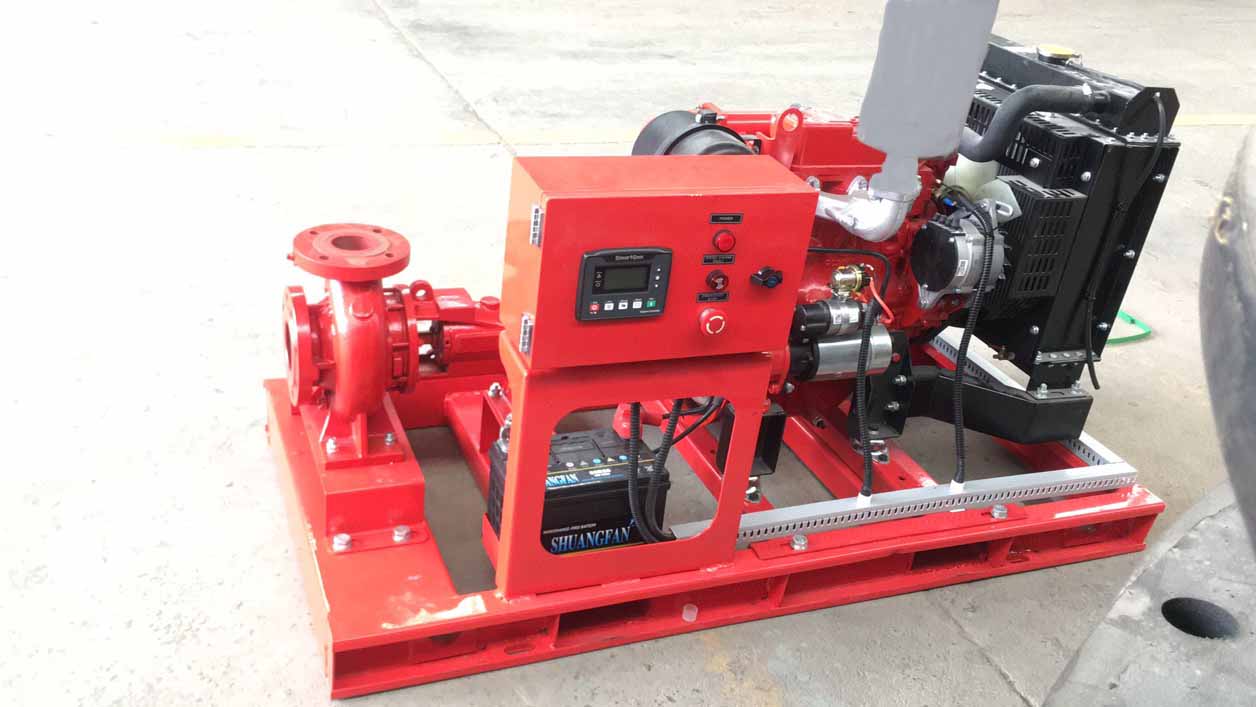
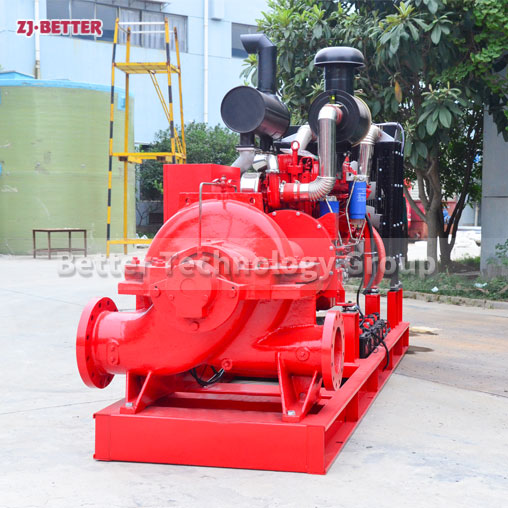
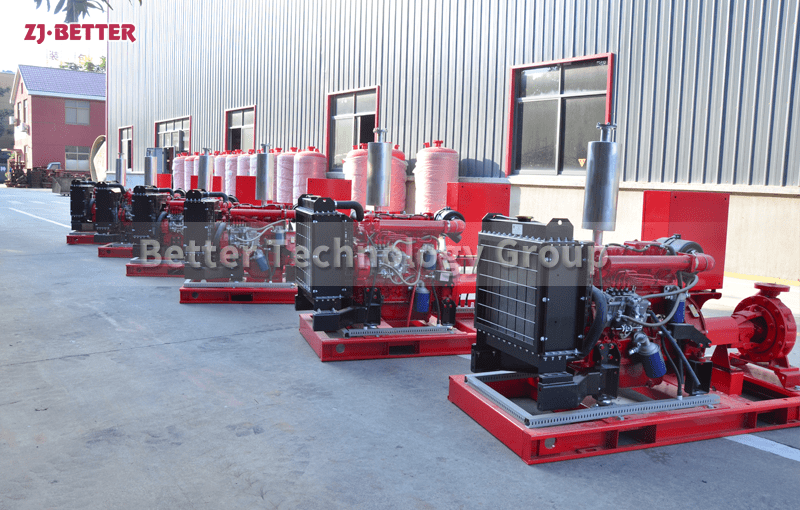
Diesel engine fire pump automatic start fast
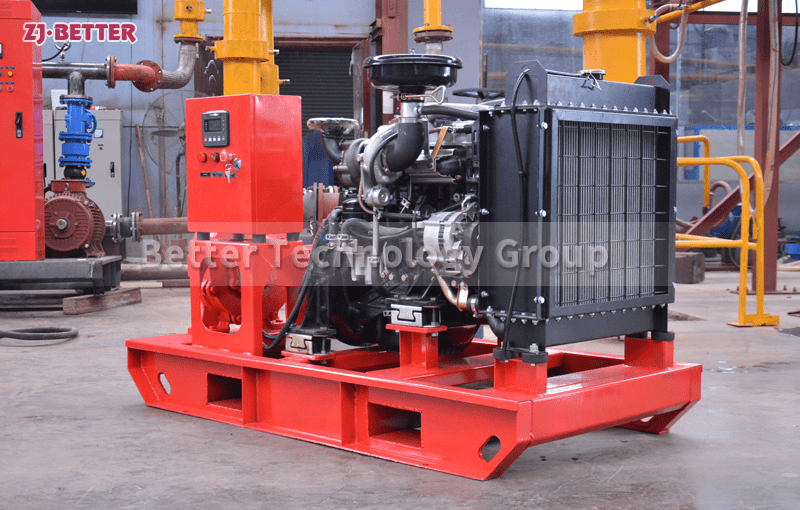
Diesel engine fire pump has the advantages of light weight, small size, flexible movement, fast start, fast water discharge time, large fuel tank capacity, corrosion resistance, reliable use, convenient maintenance, fast automatic start, self-starting, and can be refueled after dry operation . Heavy-duty pump bearings last longer; other components are made of high-quality copper and stainless steel or customer. Diesel engine fire pump high efficiency open impeller design can handle large solids and abrasives while maintaining high flow rates and high volume air handling for use in more “well point dewatering projects”.
The casing of a diesel fire pump is a pump working chamber. The impeller, shaft and rolling bearings are the rotors of the pump. The supporting part of the suspension bearing part supports the rotor part of the pump, and the rolling bearing is subjected to the radial and axial forces of the pump. In order to balance the axial force of the diesel engine fire pump, most of the impellers of the pumps have sealing rings at the front and back, and there are balance holes on the impeller rear cover. Due to the small axial force of some pumps, there is no sealing ring on the back of the impeller. and balance holes. The axial sealing ring of the diesel engine fire pump is composed of a packing pressure cover, a packing ring and a packing ring to prevent air intake or large leakage.