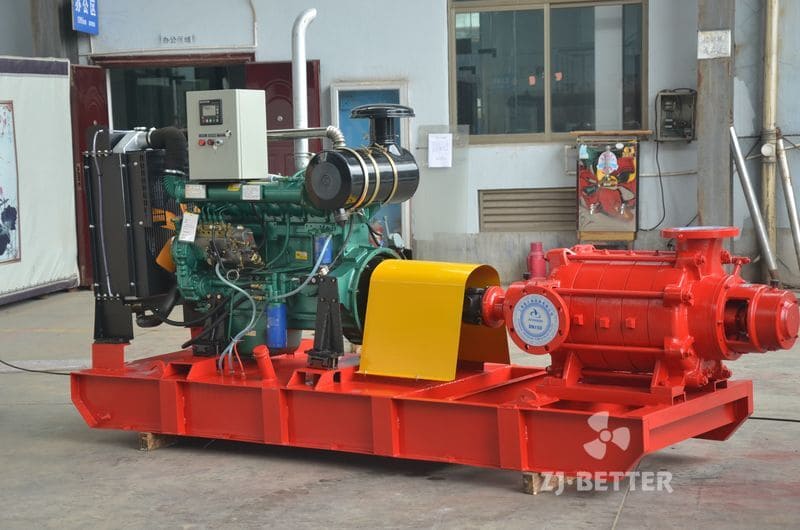
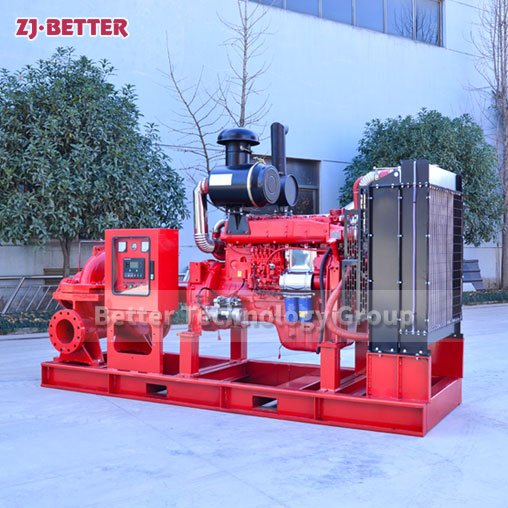
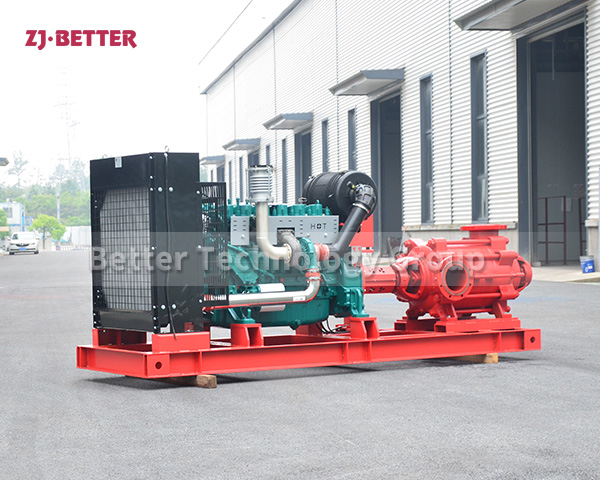
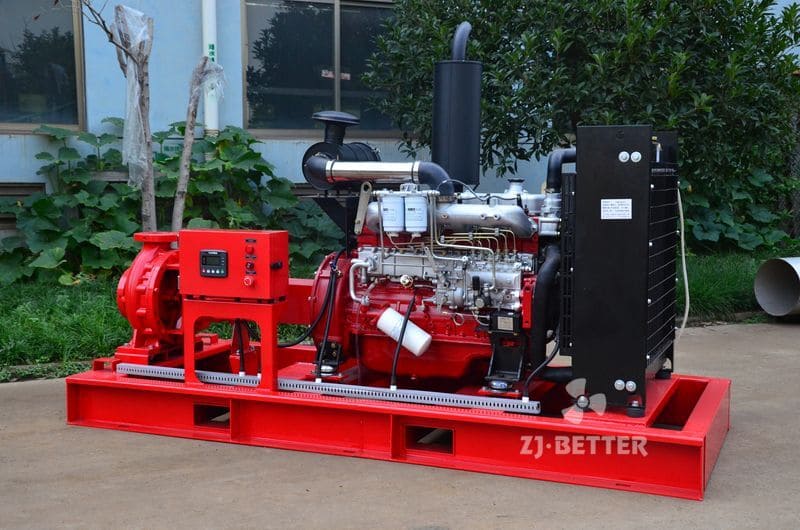
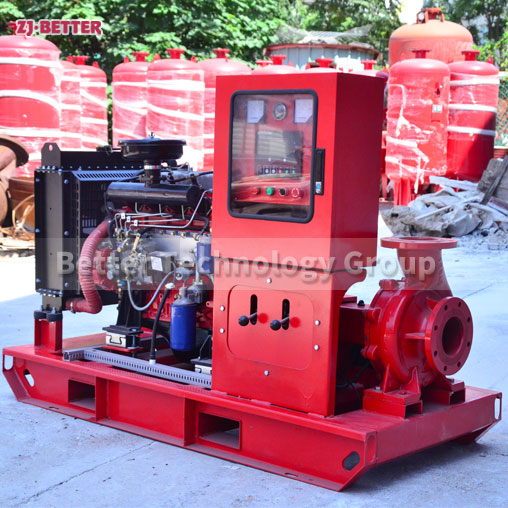
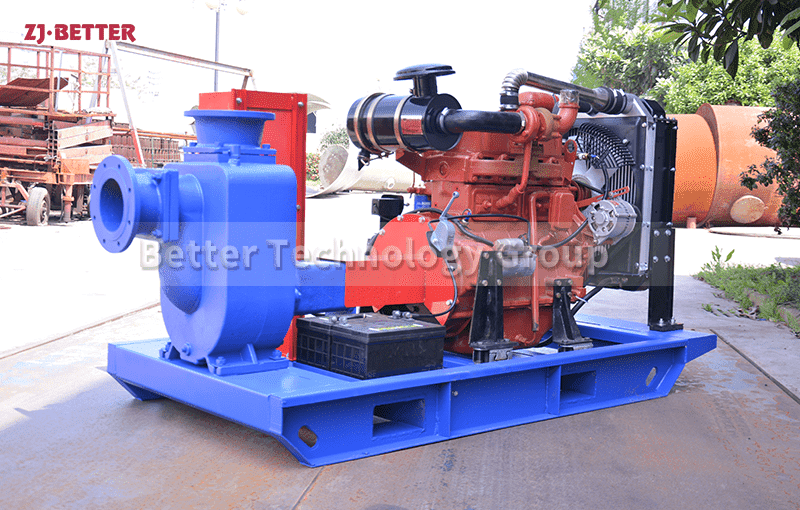
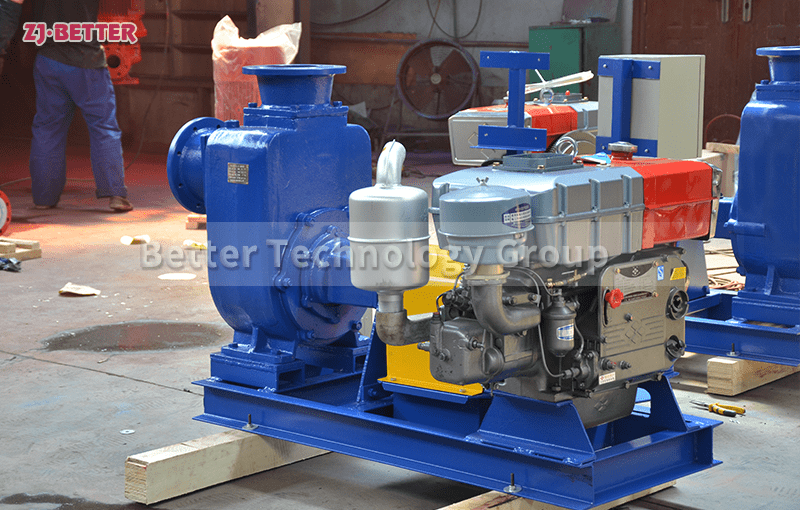
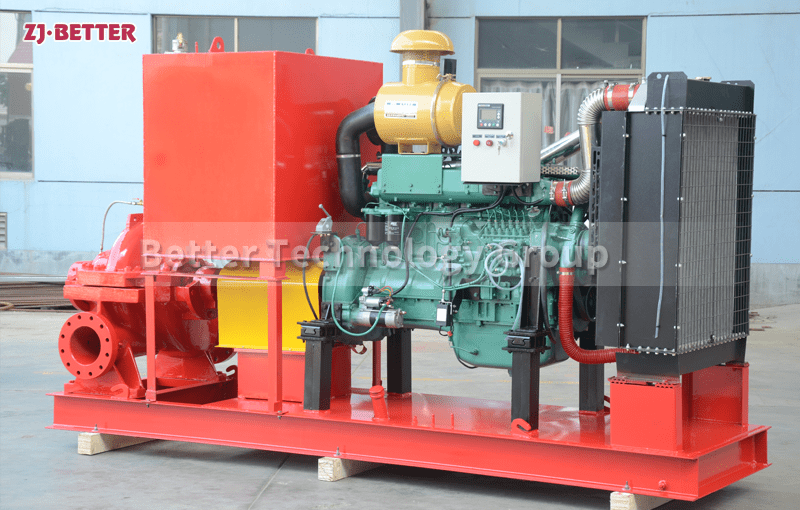
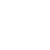
Diesel Engine Fire Pumps by Bader Manufacturers
Fire pumps typically use two driving forces, including a diesel engine and an electric motor. Diesel engines are commonly used in portable fire pumps and light duty firefighting. Electric motors are the most widely used driving force for fire pumps and are both efficient and convenient. In 2016, electric fire pumps accounted for around 50% of the entire fire pump market. Fire pumps can be used in industrial, commercial, field emergencies and more.
The casing of the diesel engine fire pump constitutes the working chamber of the pump. The impeller, shaft and rolling bearing are the rotors of the pump. The suspension bearing part supports the rotor part of the pump, and the rolling bearing receives the radial and axial forces of the pump. In order to balance the axial force of the diesel engine fire pump, most pumps are provided with sealing rings at the front and rear of the impeller, and a balance hole is provided on the back cover of the impeller. Due to the small axial force of some pumps, there is no seal on the back of the impeller. Ring and balance hole. The axial sealing ring of the diesel engine fire pump is composed of a packing gland, a packing ring and a packing to prevent air intake or a large amount of water leakage.