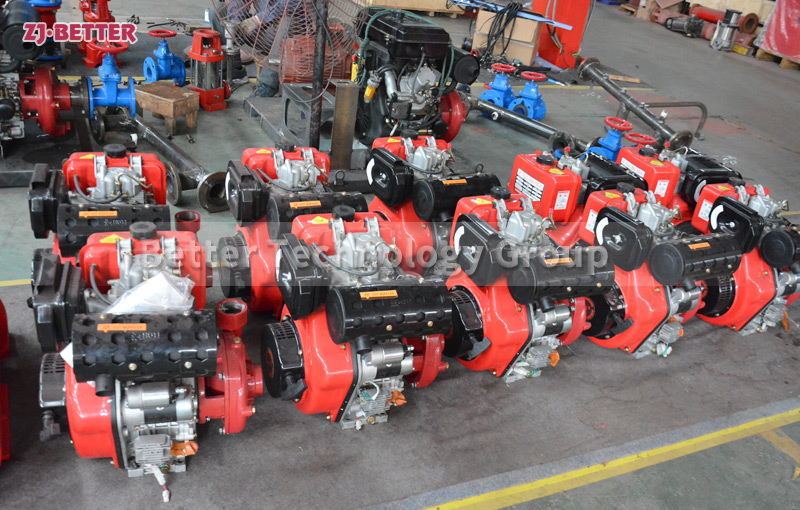
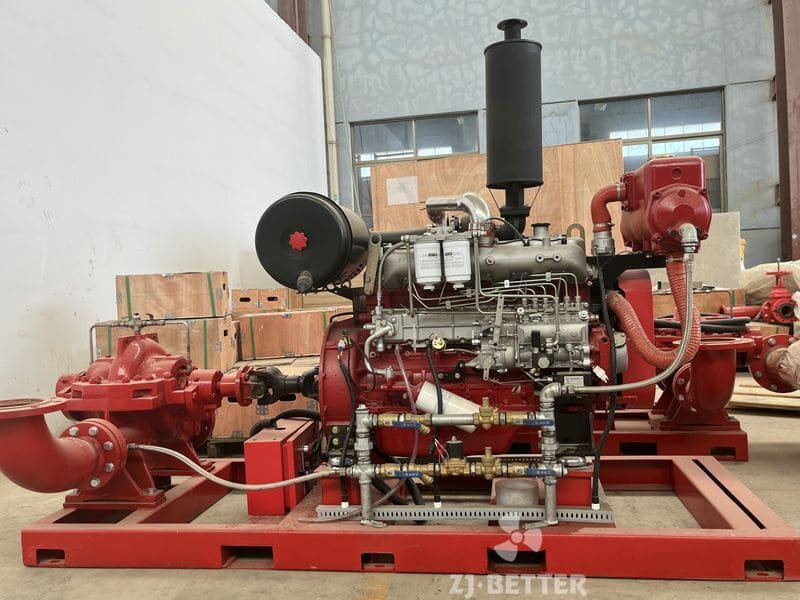
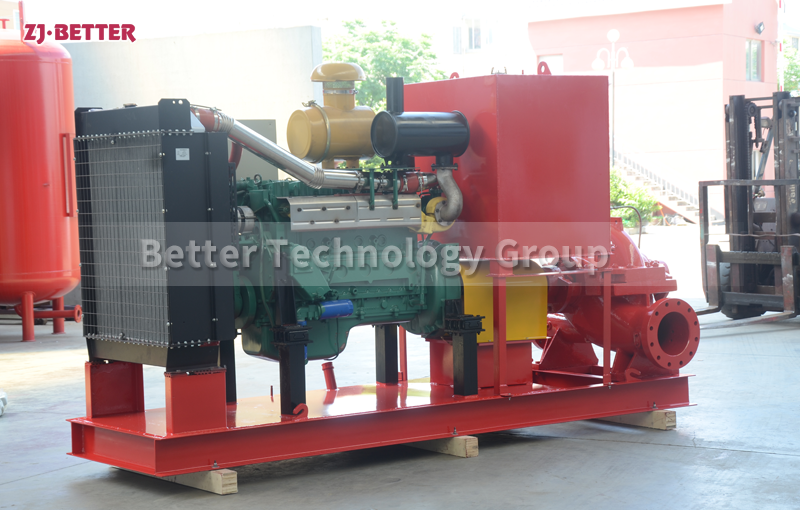
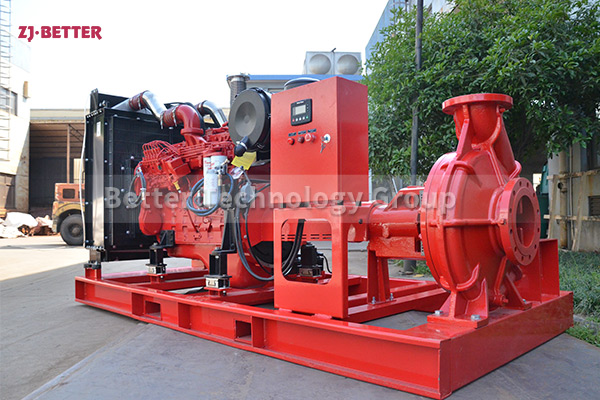
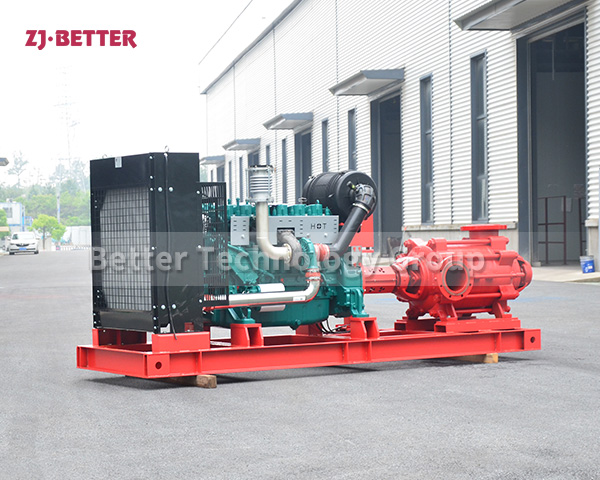
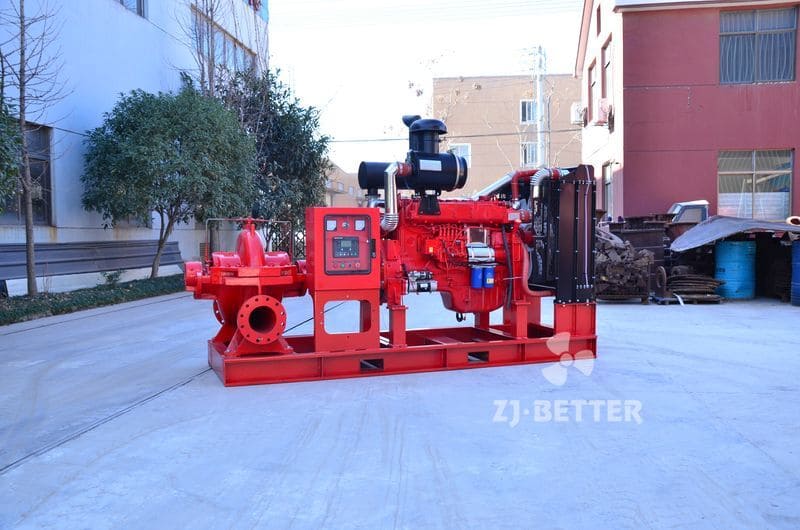
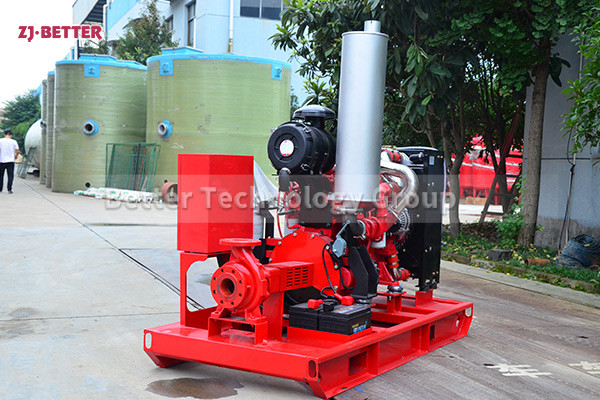
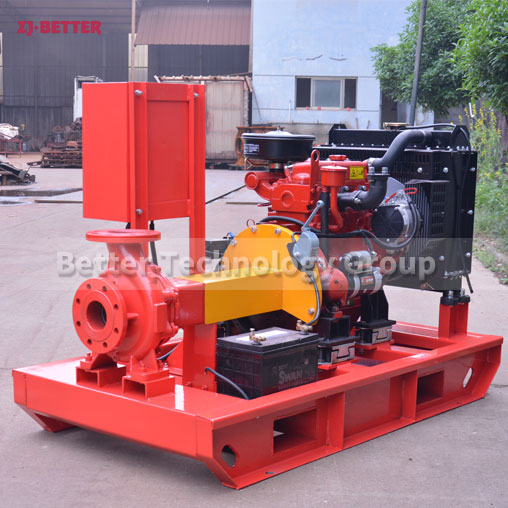
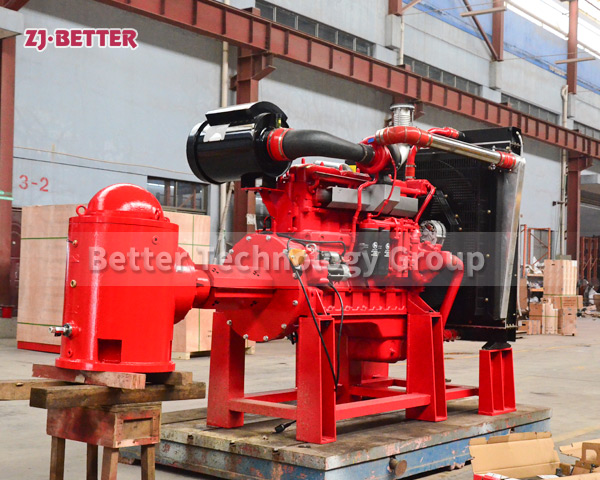
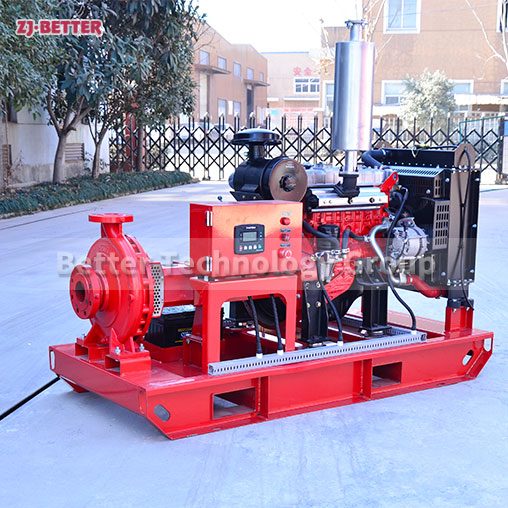
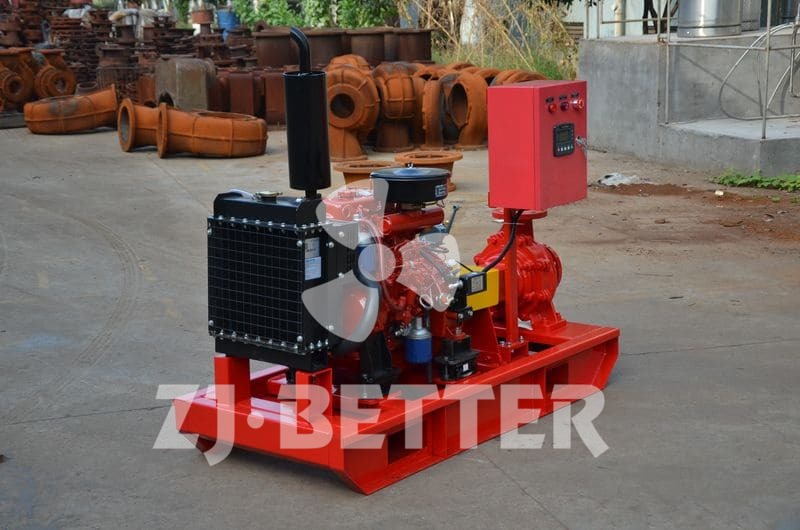
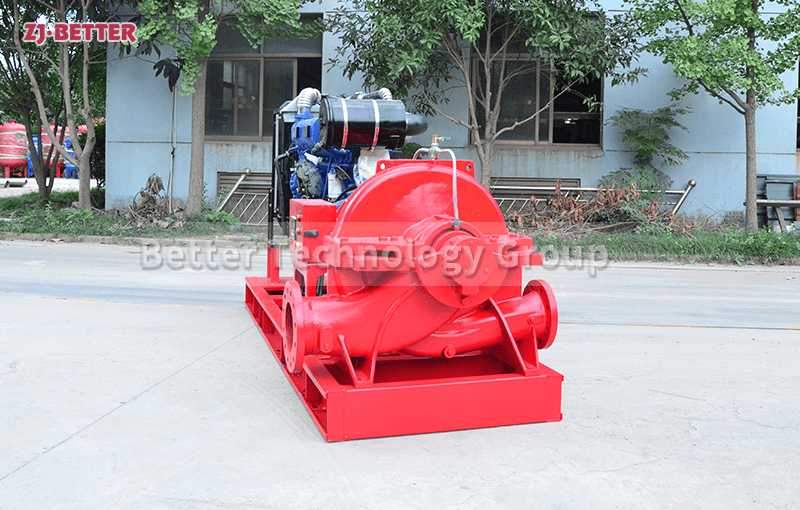
Diesel engine pump has the characteristics of small size and small footprint
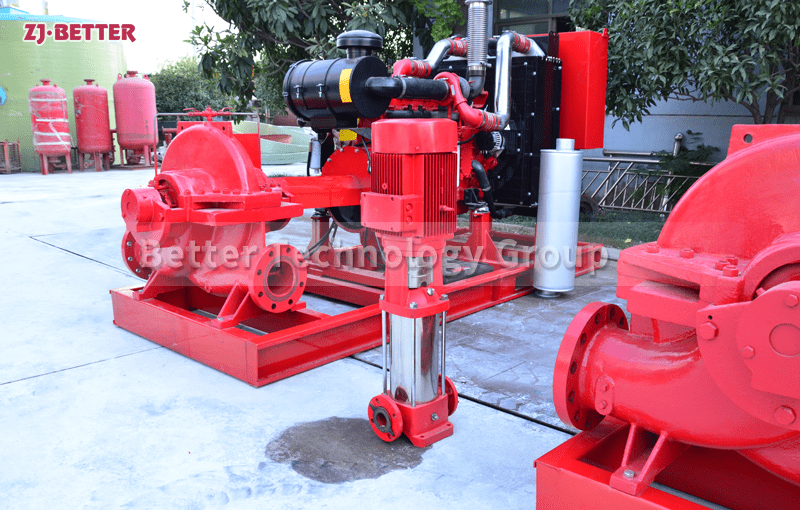
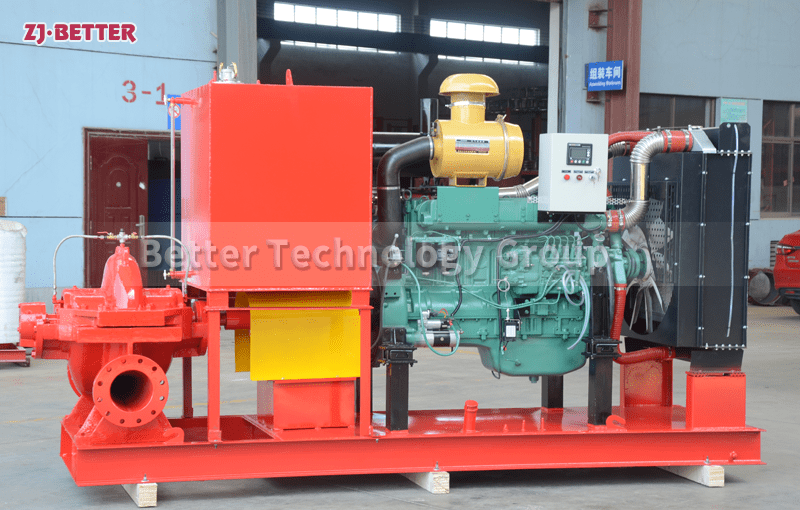
The diesel engine fire pump has compact structure, small size and beautiful appearance. Its vertical structure determines that the installation area is small, and its center of gravity coincides with the center of the pump foot, thus enhancing the running stability and service life of the pump. The horizontal direction simplifies the connection of the pipeline, the pump rotor has a small winding, stable operation, low vibration, low noise and long service life. Diesel engine fire pump is mainly used for pressurized water supply in fire protection system pipelines, and can also be used in industrial and urban water supply and drainage, high-rise building pressurized water supply, long-distance water supply, heating, bathroom, boiler cold and warm water circulation pressurized air conditioning refrigeration system water supply and equipment matching, etc. occasion.
The main heat dissipation methods of diesel engine fire pumps can be divided into two types: wind heat dissipation and water heat dissipation. According to the two heat dissipation principles, the water heat dissipation system dissipates heat evenly and has a good heat dissipation effect. The relative price is also relatively low, so most diesel fire pumps mainly use water for heat dissipation. Wind cooling is divided into two types: natural wind and forced wind. Natural wind is to use the airflow coming in from the machine during movement to directly cool the cylinder head, cylinder block and other parts; The airflow at the place increases the cooling rate and area. The principle of water heat dissipation is to use water or antifreeze as a cooling medium to take away the heat of the high-temperature parts of the diesel fire pump engine to ensure the normal working temperature of the engine.