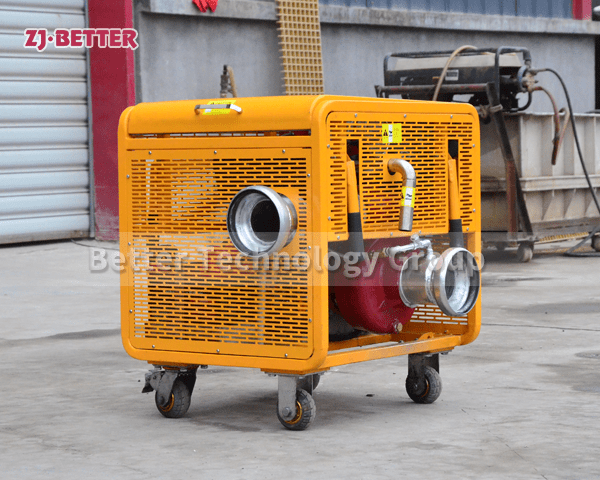
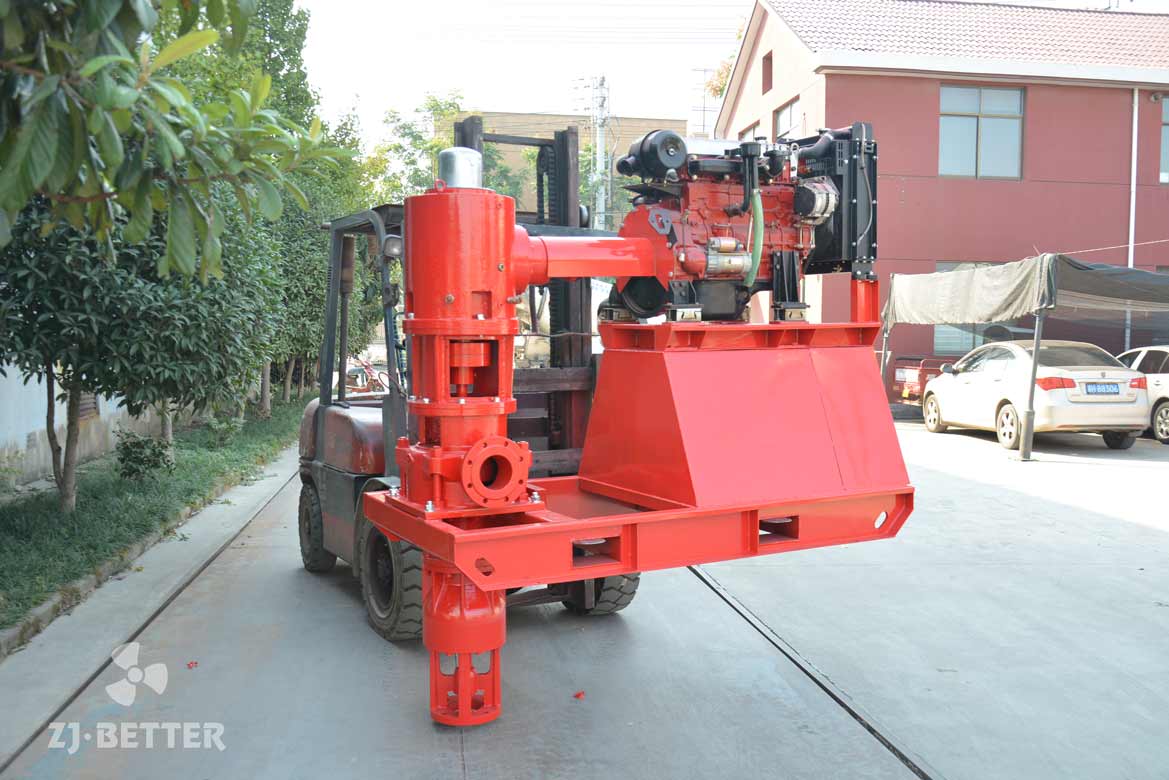
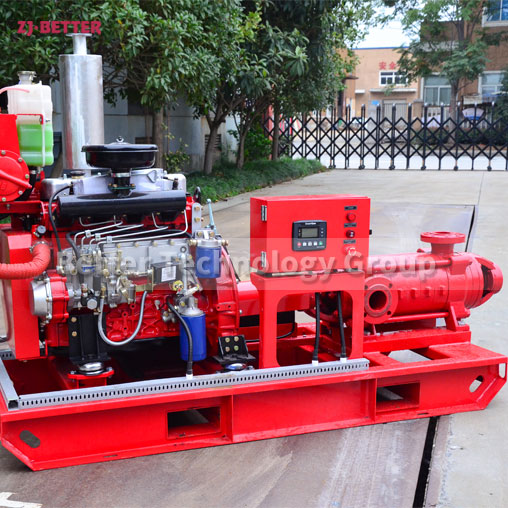
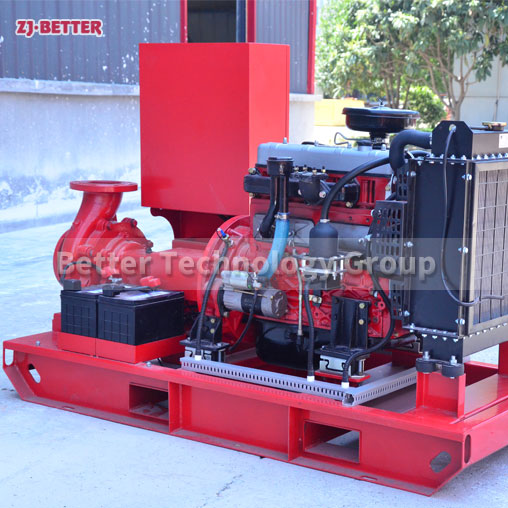
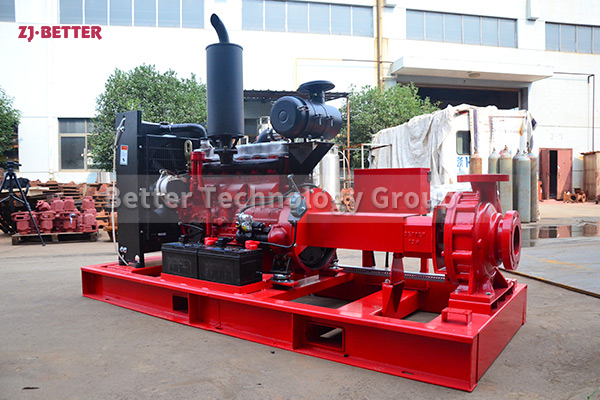
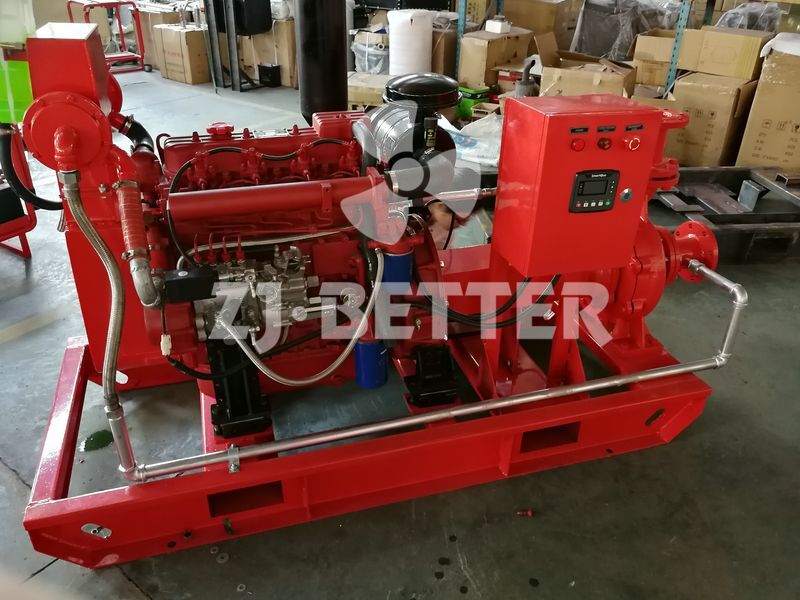
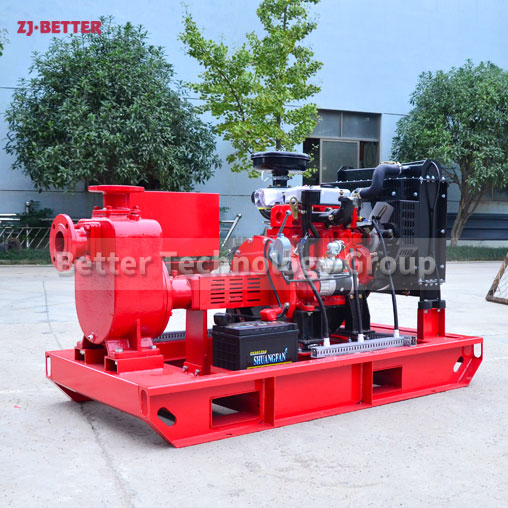
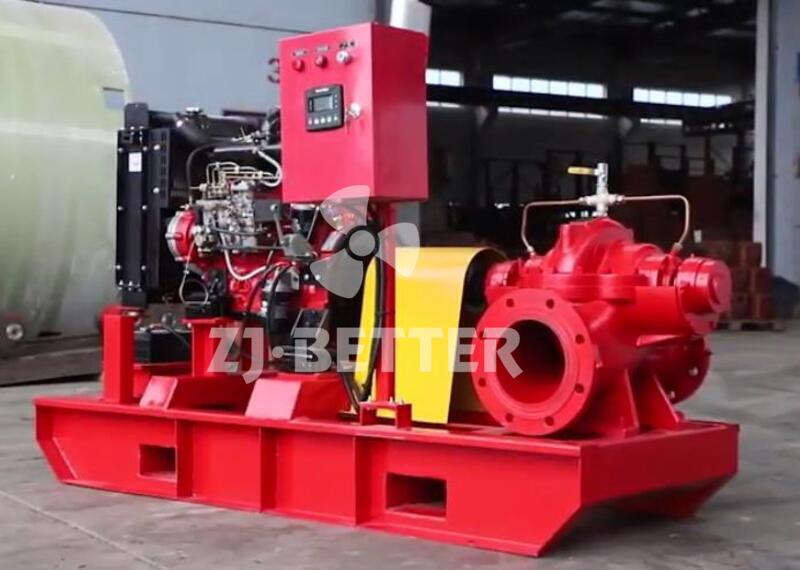
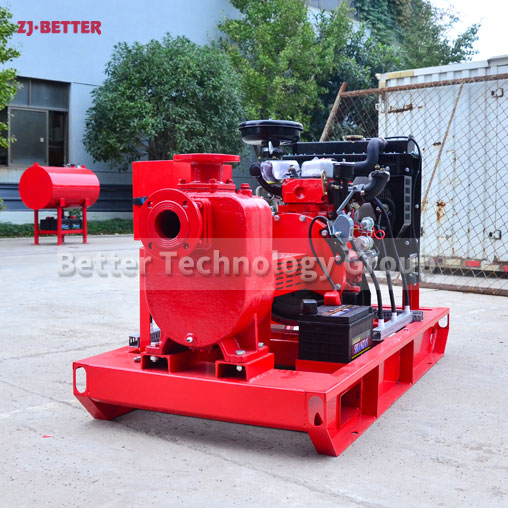
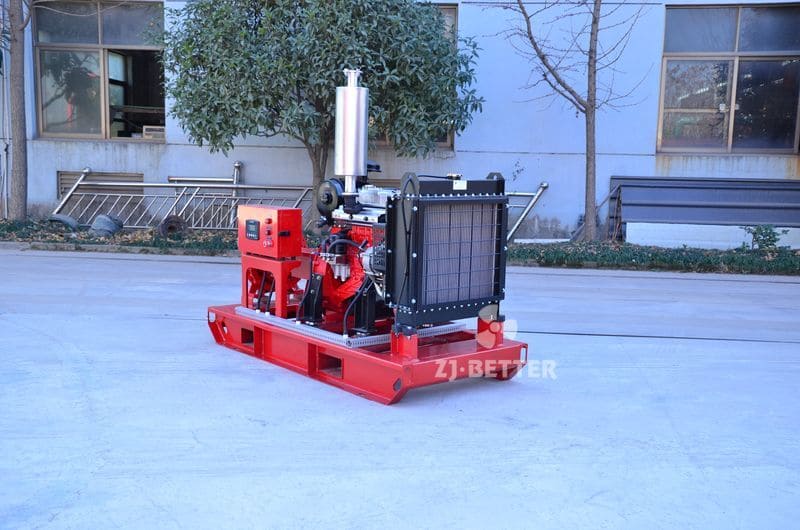
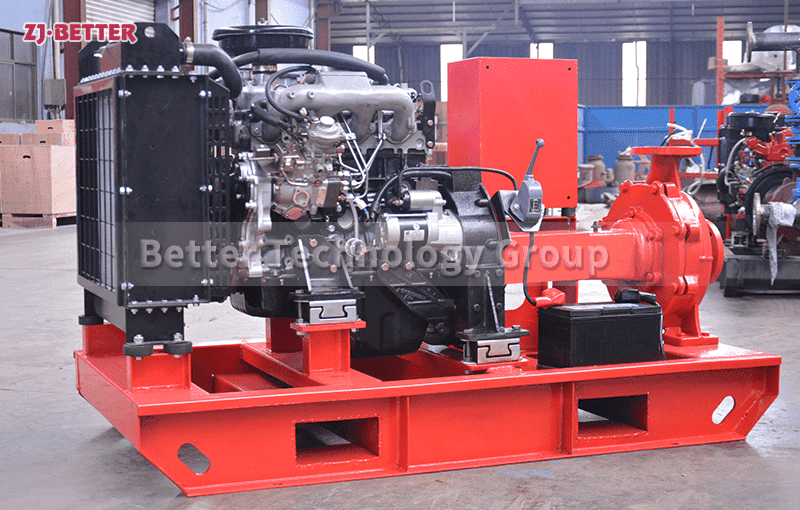
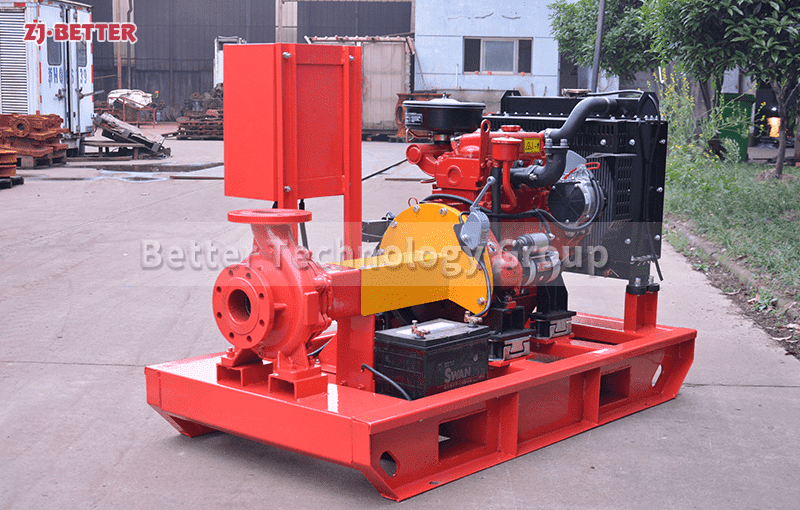
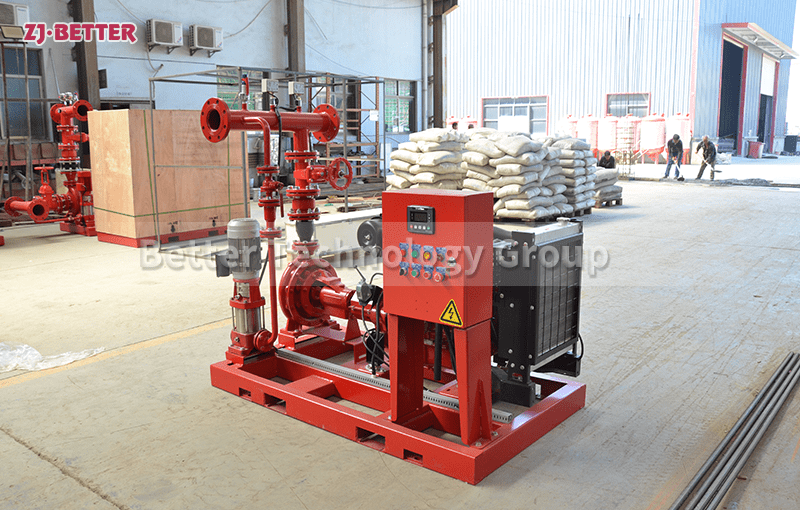
Starting and operating a diesel engine fire pump in a low-temperature environment requires special attention to ensure proper functionality and prevent potential issues. Here are some key considerations for starting and operating a diesel engine fire pump in cold weather:
Preheating: Preheating the diesel engine is crucial in cold temperatures to facilitate easier starting. Use the engine’s preheating system, if available, to warm up the engine block and aid in combustion. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for the recommended preheating duration and procedures.
Fuel Quality: Ensure that the diesel fuel used in the fire pump is suitable for low-temperature conditions. Diesel fuel can gel or become thicker in cold temperatures, which can impede fuel flow and affect engine performance. Use a winter-grade diesel fuel or a fuel additive designed to prevent fuel gelling. Regularly monitor fuel quality and maintain fuel tanks in insulated areas, if possible.
Battery Maintenance: Cold temperatures can reduce battery performance and make it more challenging to start the engine. Ensure the batteries are fully charged and in good condition. Consider using cold-weather batteries or battery blankets to maintain optimal battery temperature. Regularly check and clean battery terminals to prevent corrosion, which can hinder electrical connections.
Engine Lubrication: Use an appropriate low-temperature engine oil with a winter viscosity rating that meets the manufacturer’s specifications. Cold temperatures can cause oil to thicken, making it difficult for the engine to start and for proper lubrication to occur. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for oil type and viscosity grade based on the expected ambient temperature.
Block Heater: If available, use a block heater to keep the engine block warm. This device keeps the coolant and engine components at a suitable temperature, making it easier to start the engine in cold weather. Ensure the block heater is properly installed and functioning correctly.
Regular Maintenance: Perform regular maintenance tasks specific to cold weather conditions. This includes checking and replacing fuel and oil filters, inspecting and cleaning air intake systems, and ensuring proper coolant levels and antifreeze concentration. Regularly inspect the engine components for any signs of wear or damage that may affect cold-weather performance.
Protection from the Elements: Protect the diesel engine fire pump from harsh weather conditions by housing it in a climate-controlled enclosure or installing insulation around critical components. This helps maintain the engine’s temperature and prevent freezing of fluids and components.
Operating Practices: During operation, allow the engine to warm up before applying heavy loads or demanding high RPMs. This allows the engine and its components to reach the optimal operating temperature gradually. Avoid sudden and aggressive acceleration or deceleration, as it can stress the engine and lead to potential damage in cold conditions.
Remember to consult the manufacturer’s recommendations and follow their specific instructions for starting and operating the diesel engine fire pump in low-temperature environments. Additionally, regular training and familiarization with the fire pump system are crucial for firefighters and operators to handle and operate the equipment effectively and safely in all weather conditions.