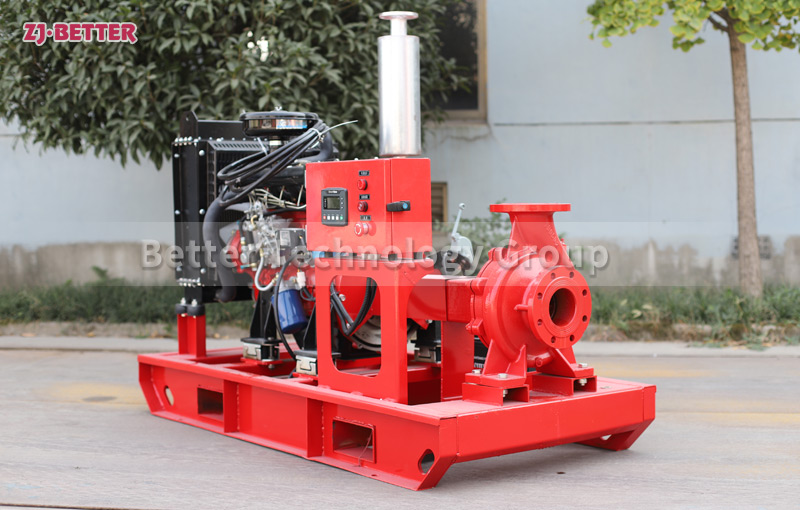
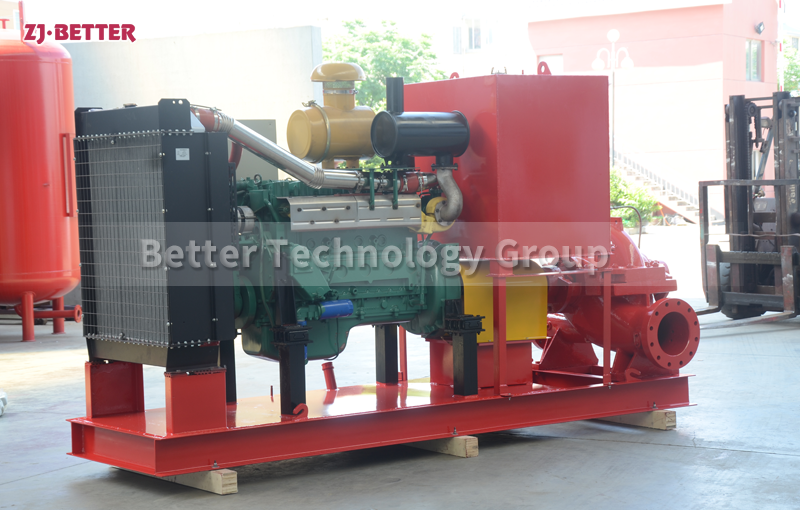
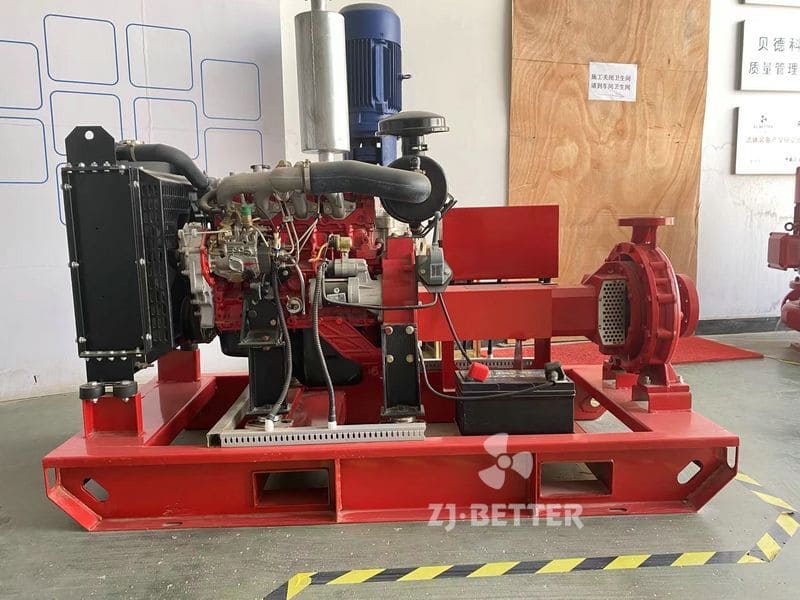
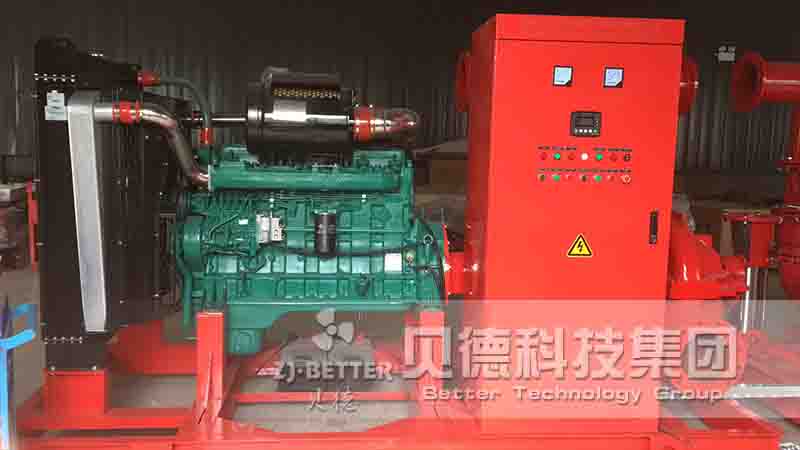
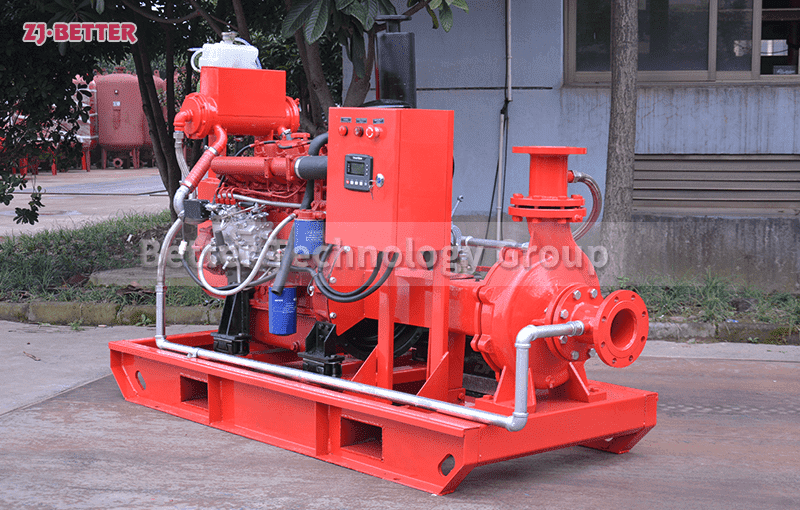
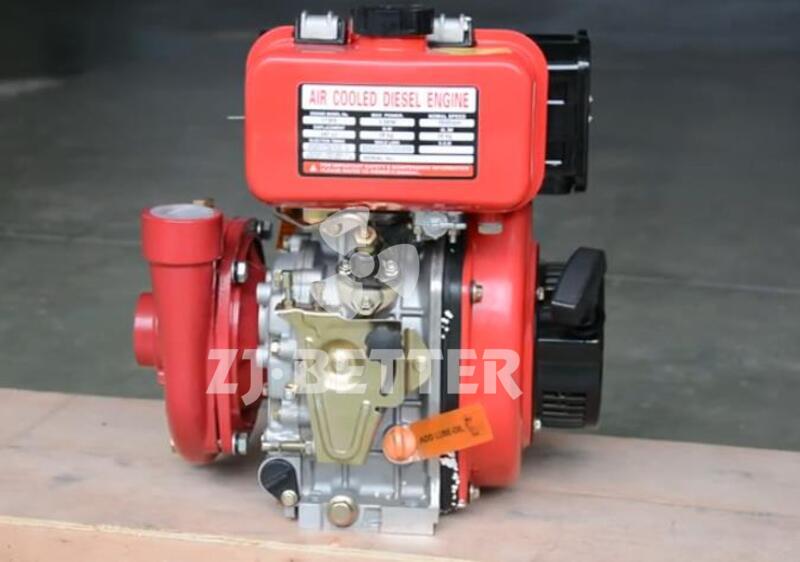
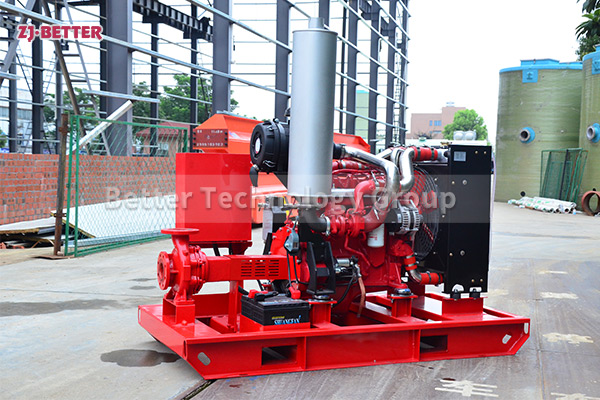
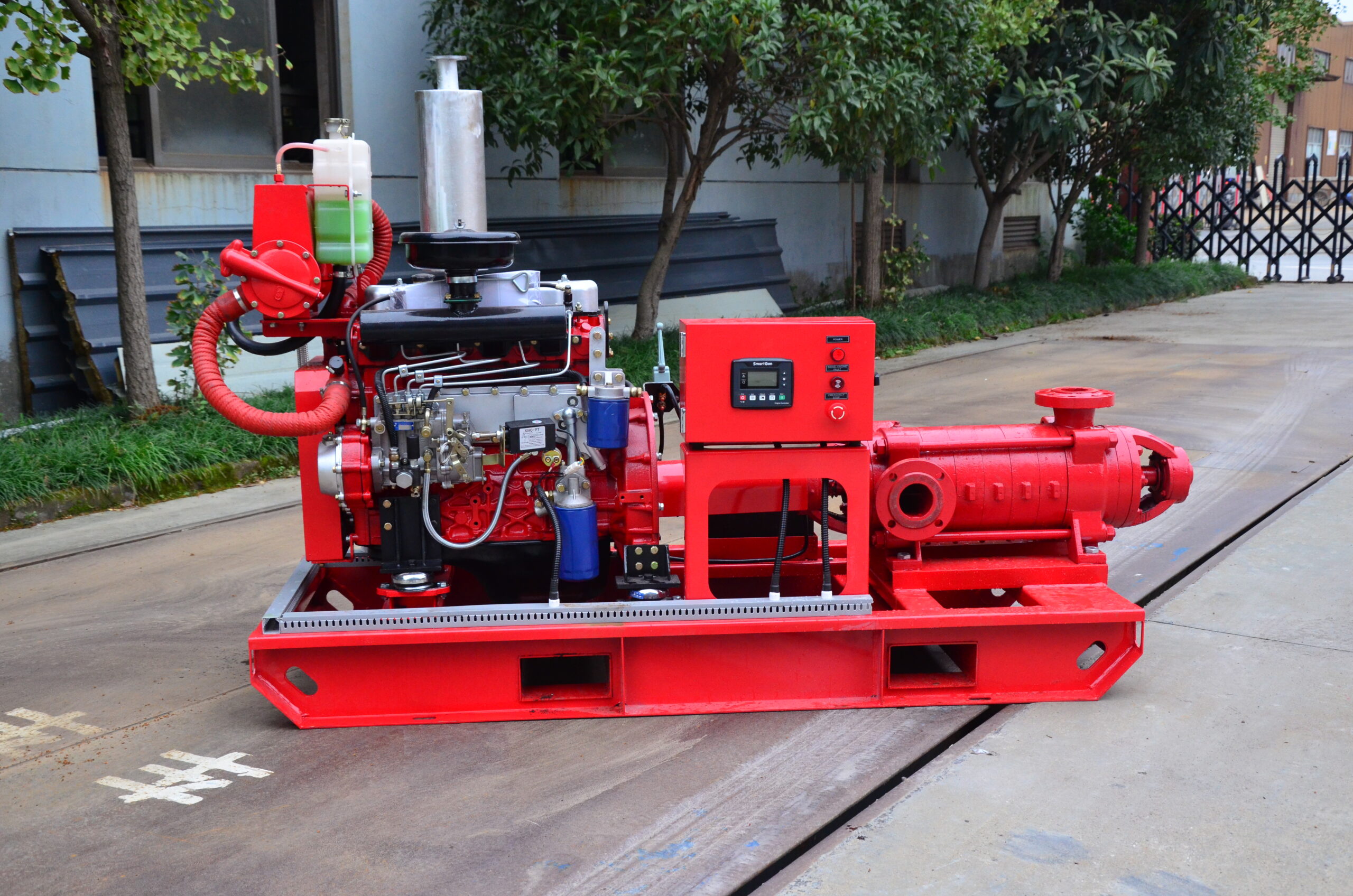
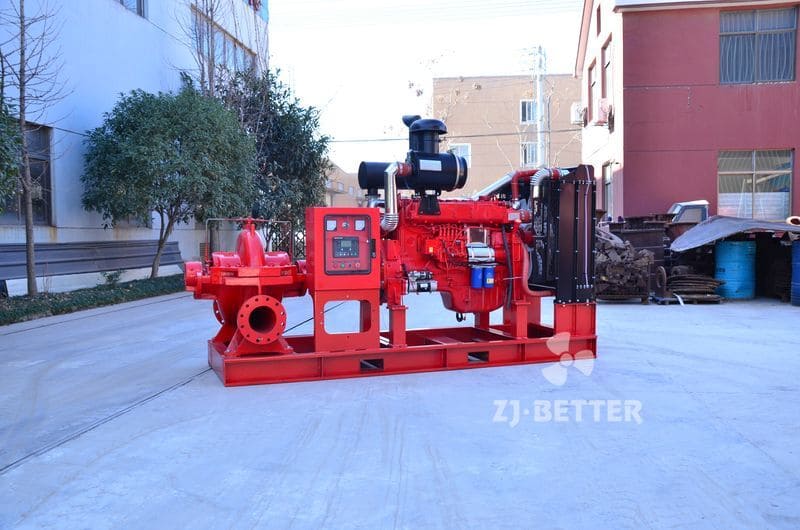
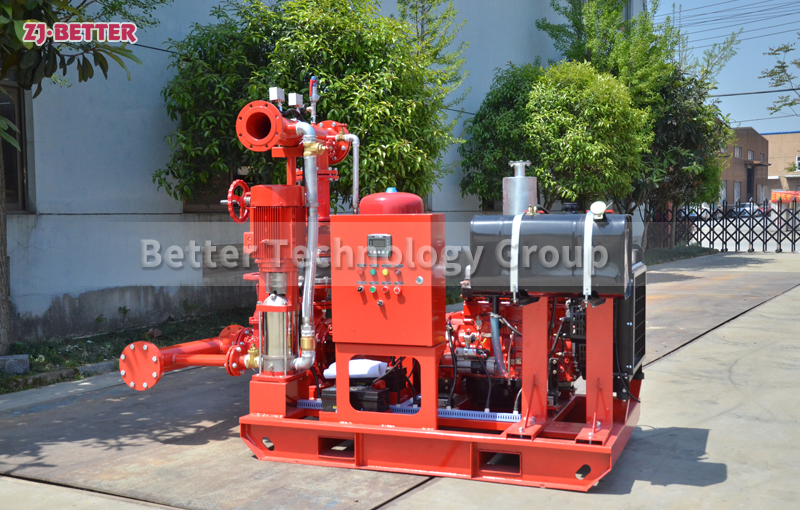
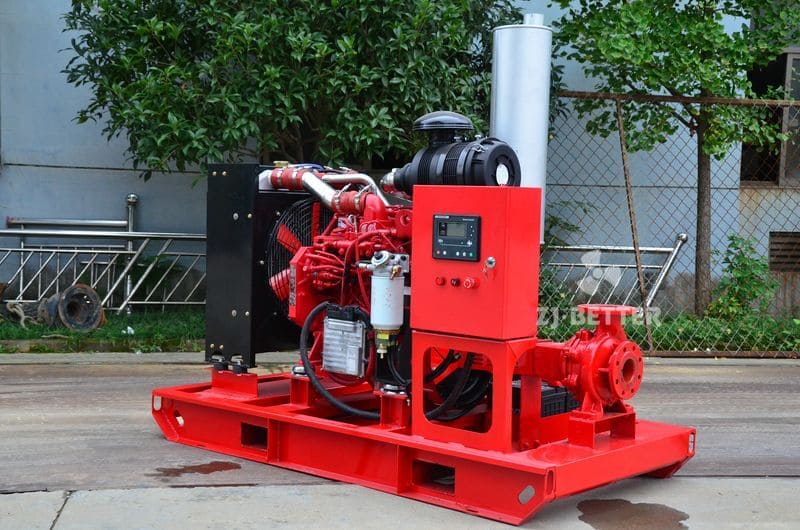
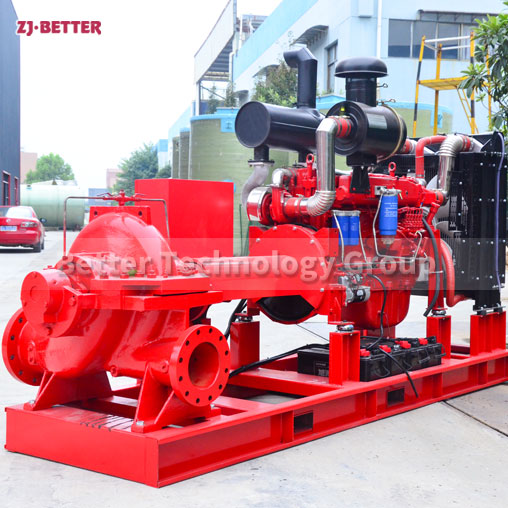
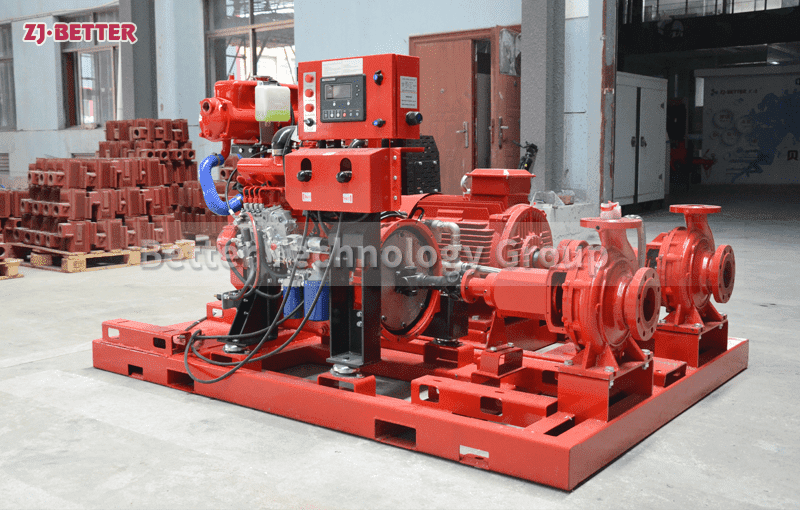
Several reasons for the high temperature of diesel engine fire pump
The engine cooling system of the diesel engine fire pump adopts double closed-loop heat exchangers. The system has the advantages of high cooling efficiency and little influence on the ambient temperature of the pump room. The cooling water flow direction is controlled by a ball valve from the pump outlet pipe to the heat exchanger, so that the cooling water temperature of the body is between 85 and 95 °C. If the water temperature is too high, the opening of the ball valve can be increased, the heat dissipation capacity of the heat exchanger can be increased, and the water temperature of the engine cooling water can be reduced. On the contrary, the opening of the ball valve can be closed to increase the water temperature of the engine cooling water.
Diesel engine fire pump sets, such as automatic control fire pump sets, add a solenoid valve in parallel with the ball valve in the heat pipe. Under normal circumstances, the solenoid valve is closed, and the cooling water can meet the engine cooling requirements through the gate valve. When the engine cooling water temperature exceeds 95°C, the solenoid valve will automatically open to increase the cooling water flow and reduce the engine cooling water temperature. After 20 seconds, when the water temperature of the diesel engine still exceeds 95°C, the automatic control system will issue an audible and visual alarm and call the staff to the scene to check the cause.
There are several reasons why the temperature of a diesel engine fire pump is too high:
1: The diesel engine fire pump is overloaded. Therefore, in the operation of the fire pump, the high-speed and overload operation of the diesel engine must be avoided.
2: The oil radiator of the diesel engine fire pump is blocked by foreign objects, resulting in poor heat dissipation;
3: The position of the oil temperature adjustment switch of the diesel engine fire pump is incorrect. In summer, the oil does not dissipate heat through the radiator;
4: The cylinder of the diesel engine fire pump leaks, and the high temperature gas enters the oil pan to heat the oil in the oil pan.
5: The cooling fan speed of the air cooler of the diesel engine fire pump is too low, which reduces the cooling intensity and increases the body temperature of the diesel engine