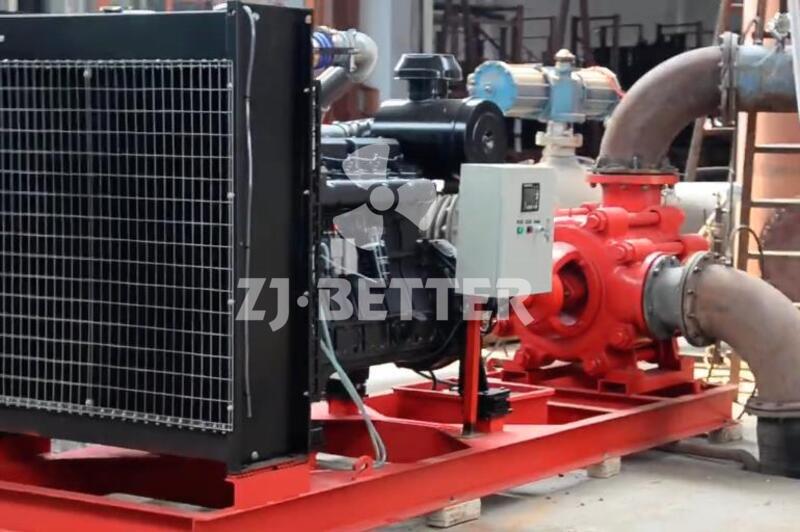
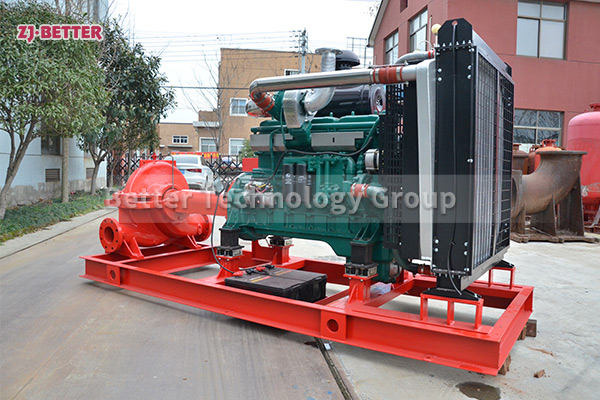
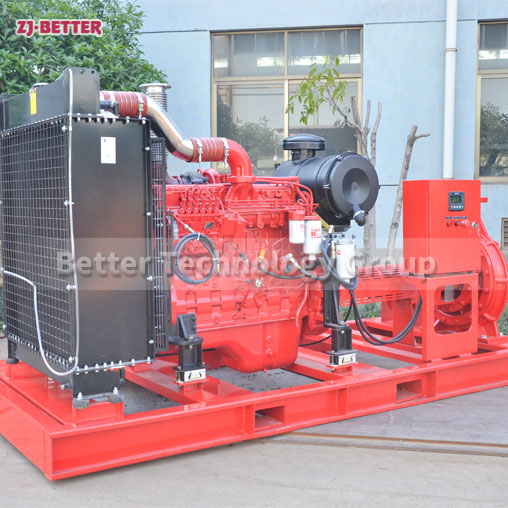
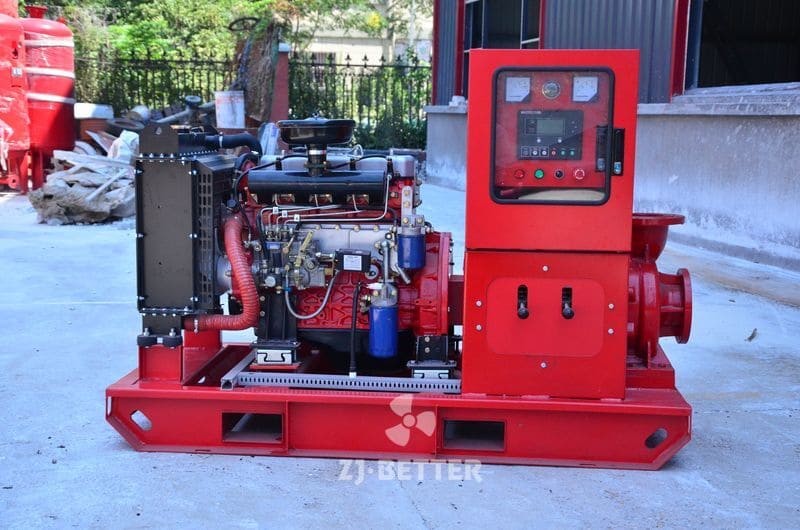
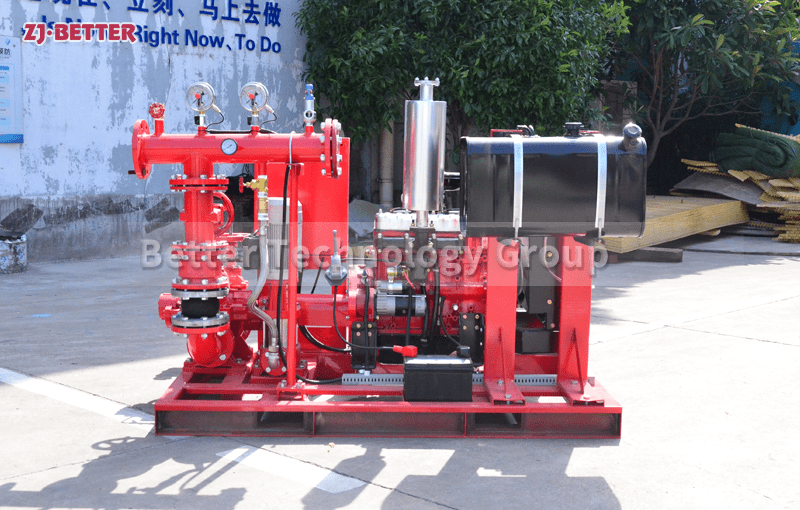
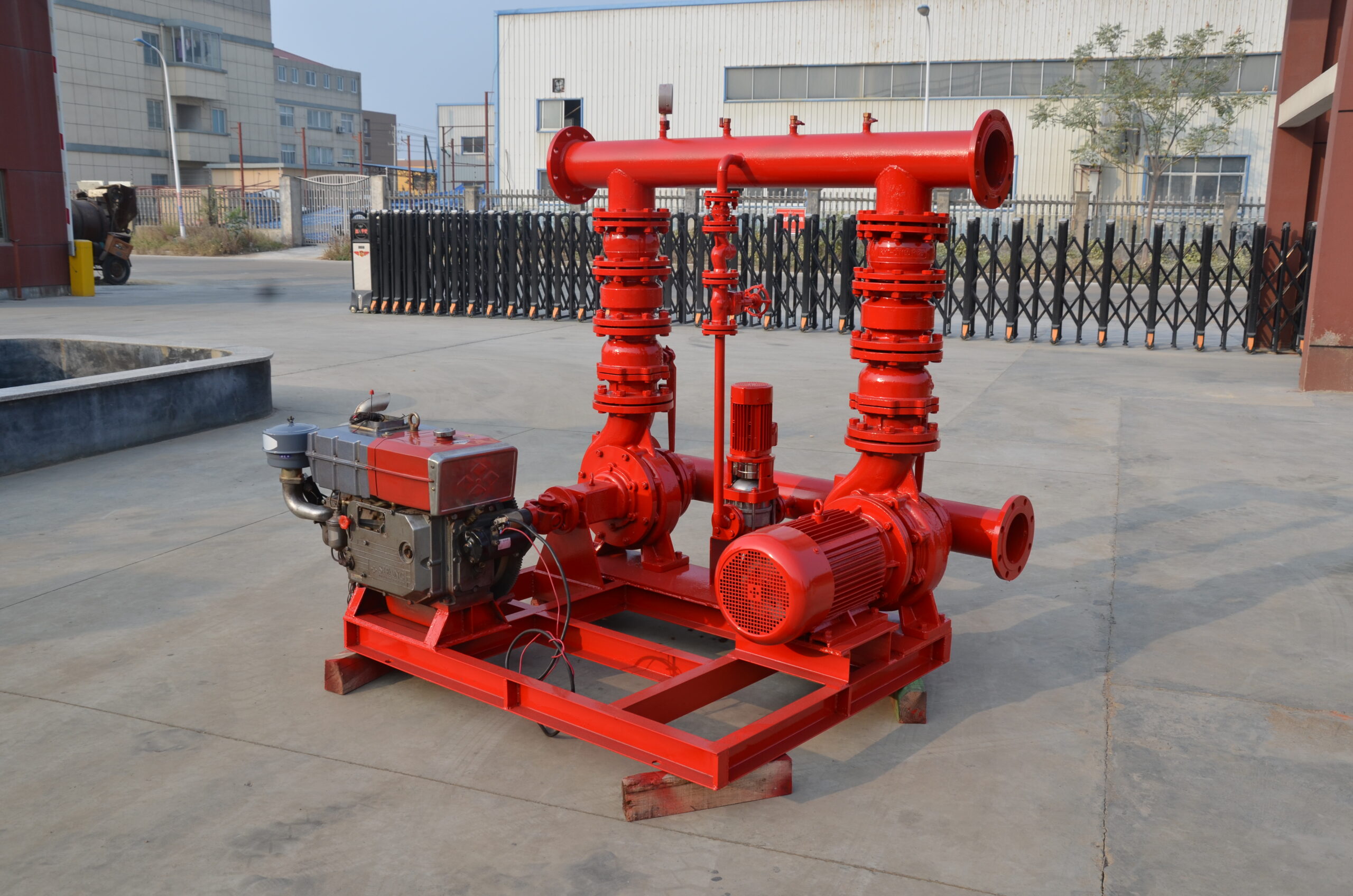
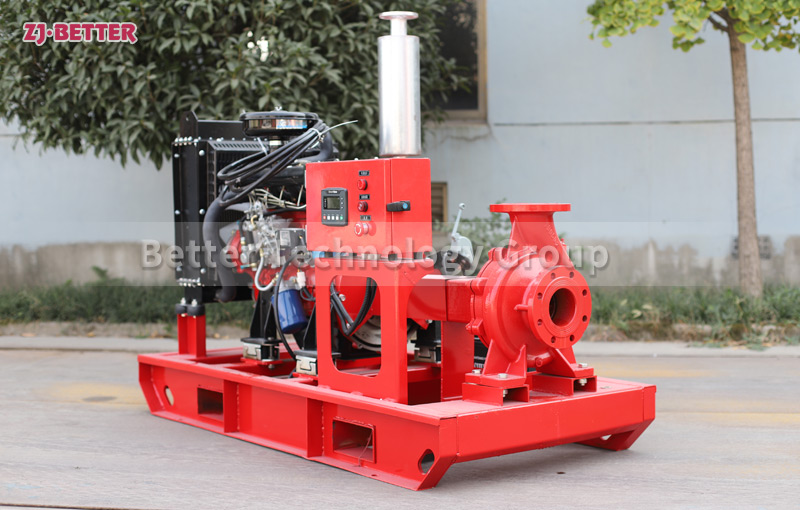
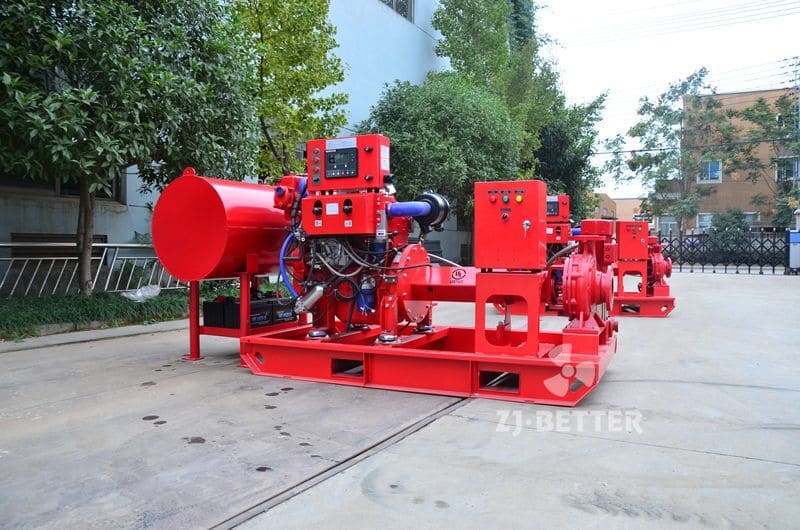
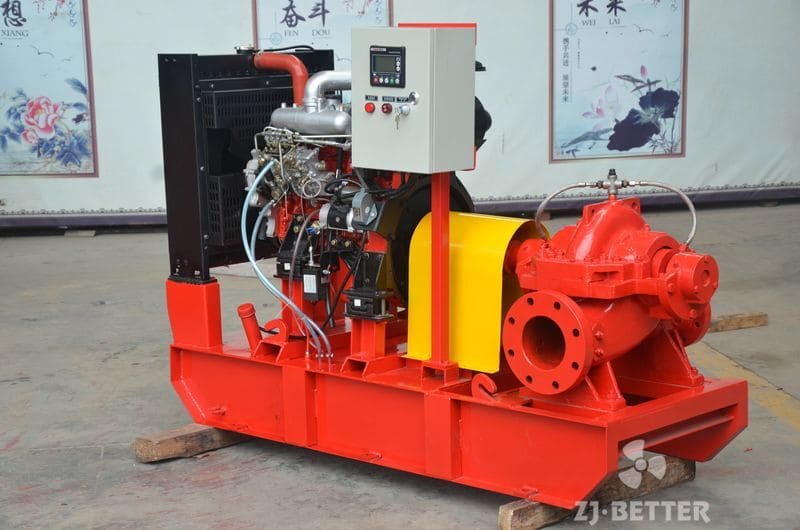
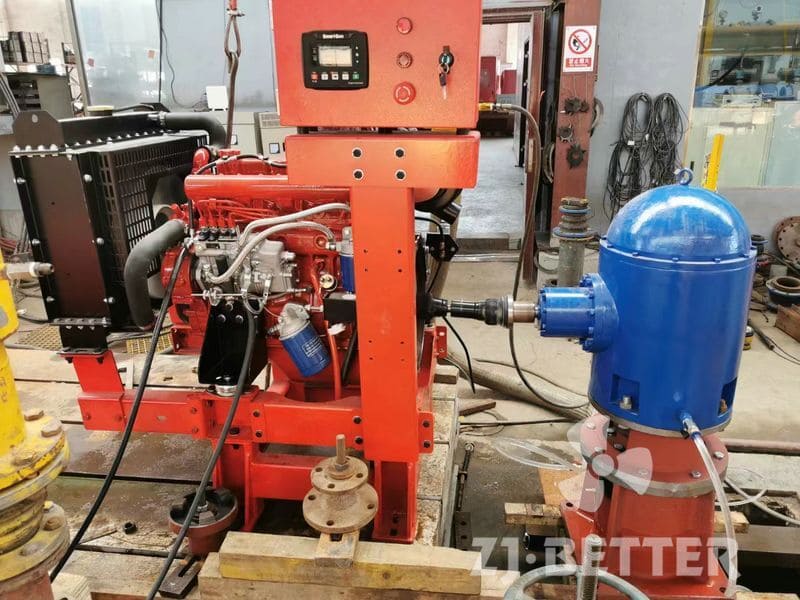
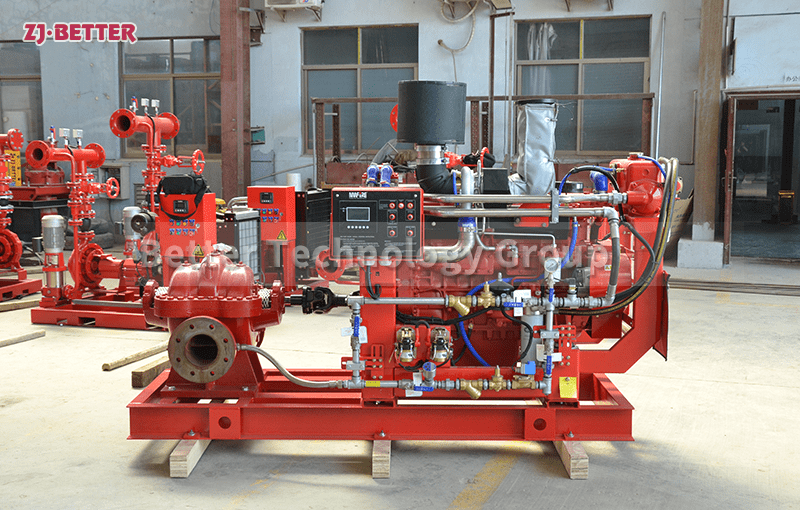
Structural features and functions of diesel engine fire pump
The diesel engine fire pump unit is directly driven by the diesel engine fire pump, and it is a mechatronic equipment that can start and complete the water supply in a short time. The diesel engine pump set is driven by a diesel engine without external power supply. Diesel pumps are suitable for fire water supply occasions such as agricultural irrigation, emergency rescue, smelting, hangars, petrochemical oil depots, power plants, liquefied gas stations, and textiles. Especially when there is no electricity and the grid is not satisfied, choosing a diesel engine-driven water pump is the safest choice.
The diesel engine fire pump set is easy to use and can be equipped with remote instruments. Access Control Center as needed. The unit is easy to use and maintain.
The diesel engine fire pump unit has high initiative, with active, manual and fault self-checking functions. The whole process of working condition monitoring can recover engine faults, actively restart the engine, and actively preheat, making the equipment start-up safer and more reliable.
The diesel engine fire pump unit has remote control and remote control functions in the central control room, and can also be connected to the field bus.
As a fixed fire fighting equipment, the diesel engine fire pump set has been widely used in fire fighting diversion. Diesel fire pump has no power or power is incorrect.