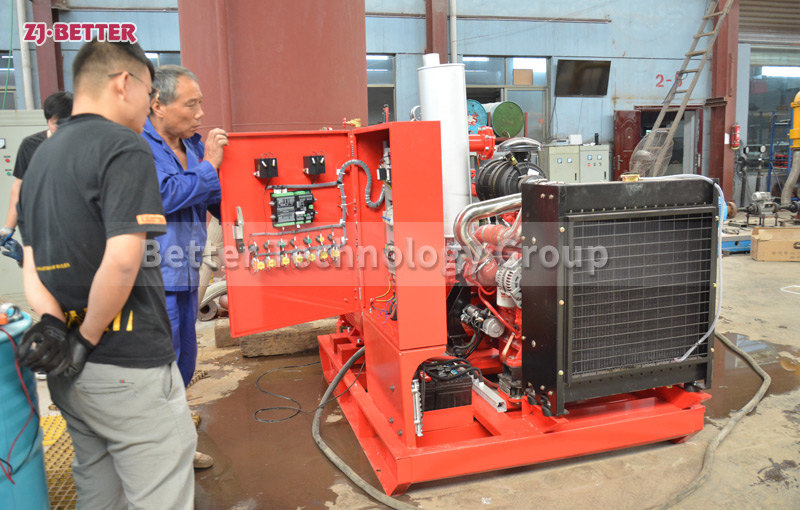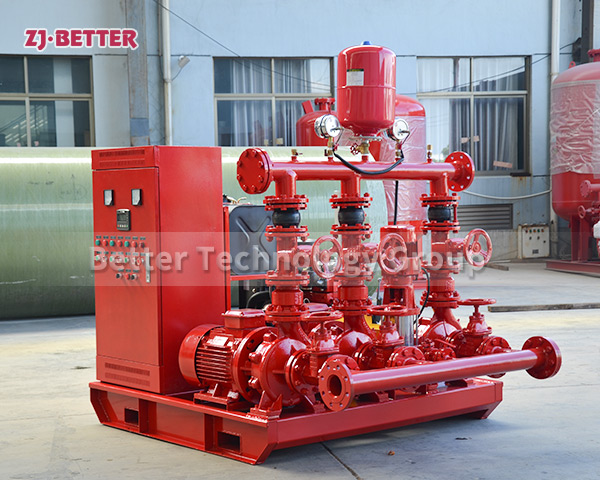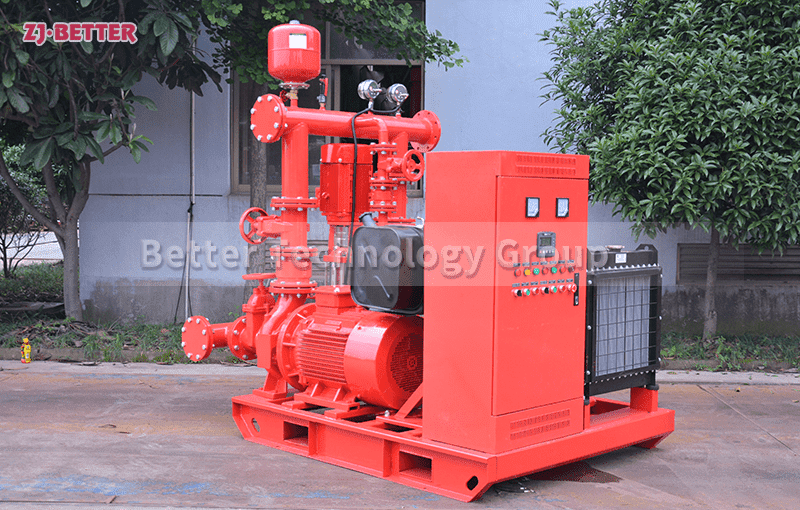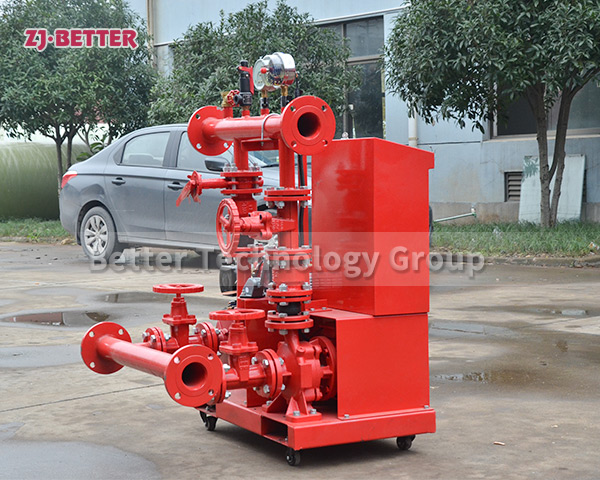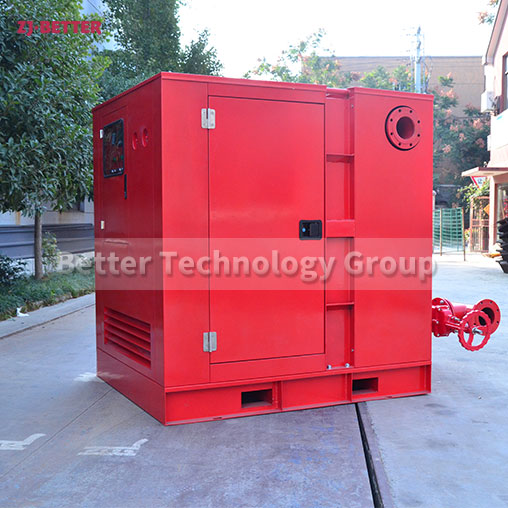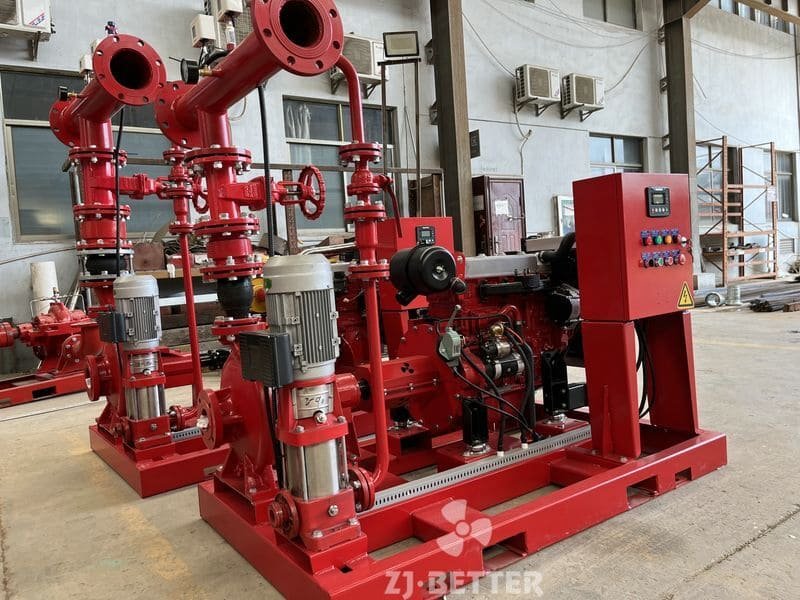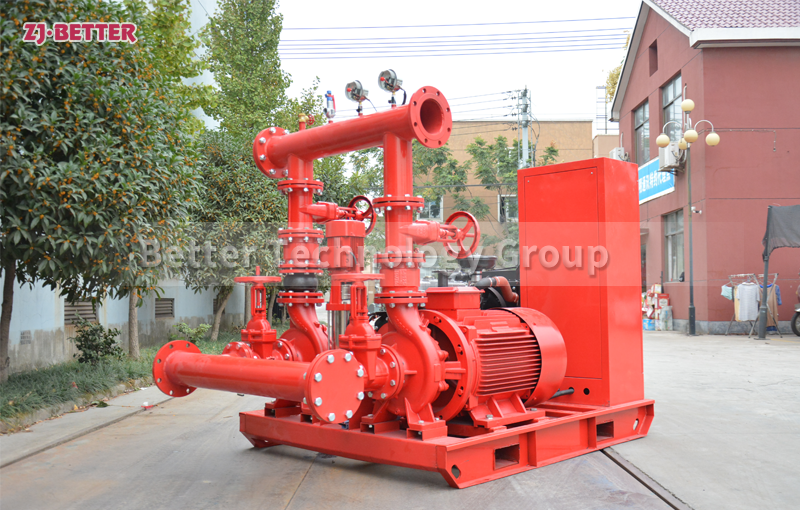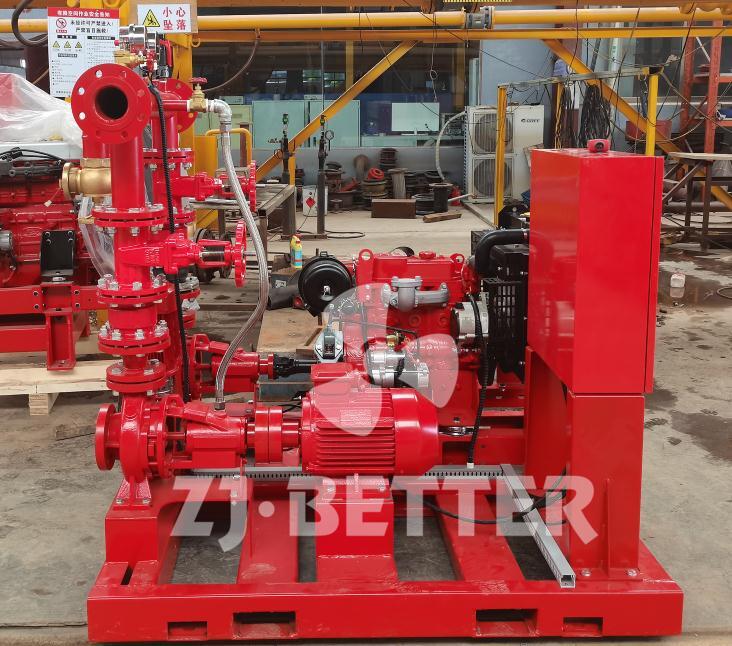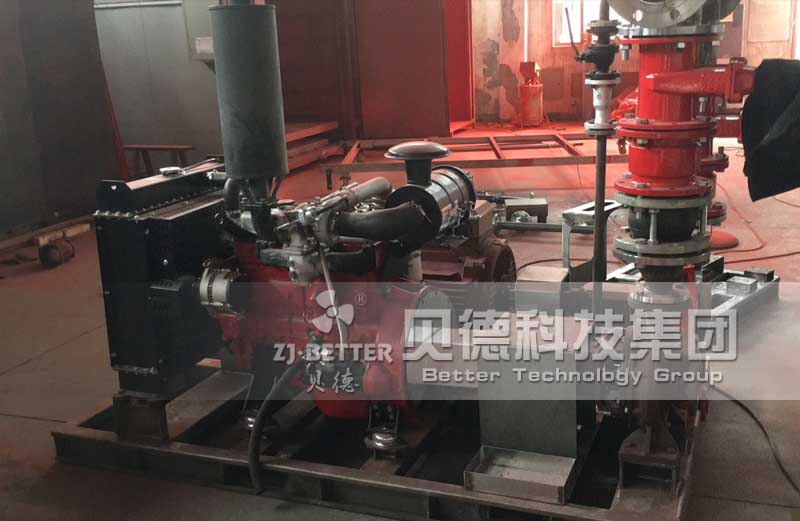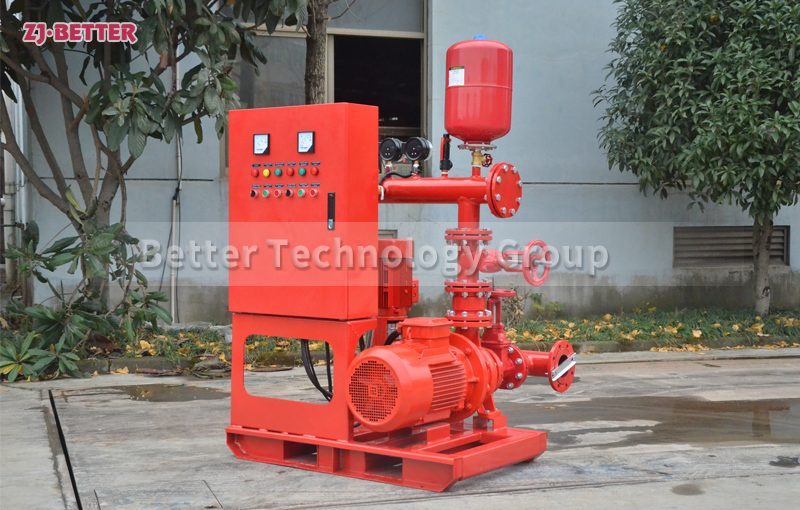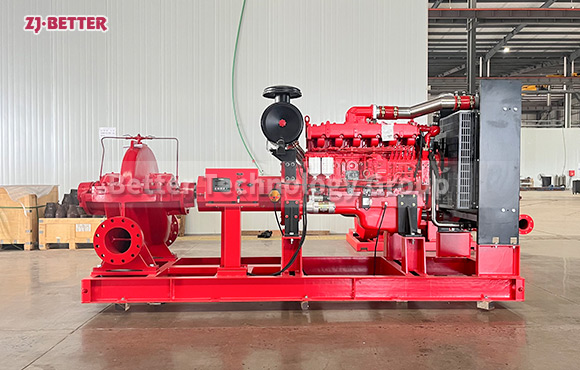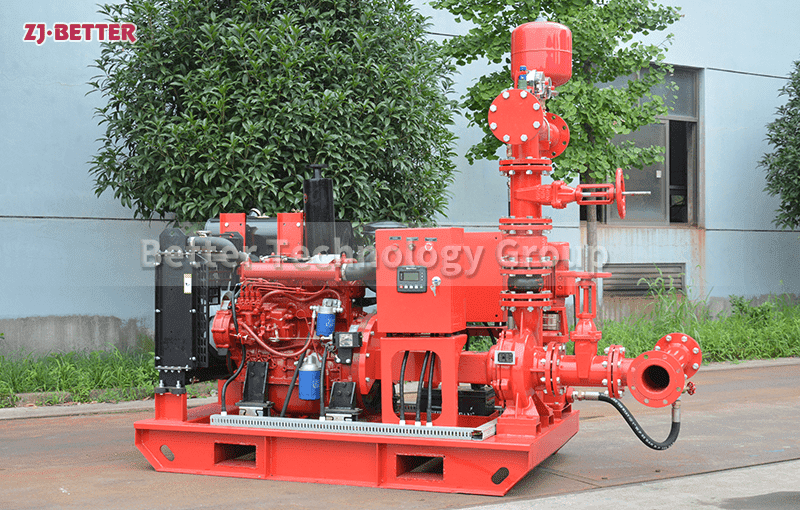
The difference between Multistage pump and single stage pump.
Multi stage pump refers to a pump with two or more impellers, which can absorb and press water in stages and stages, so as to lift the water to a very high position. The lift can increase or decrease the number of stages of pump impellers according to needs; When the single-stage pump head needs to be equipped with two-stage motors, the multi-stage pump can be equipped with four-stage motors by increasing the number of impellers, which can improve the service life of the pump and reduce the noise of the unit. When the actual required lift of the pump is less than 125 meters, the selection of a single-stage pump or a multi-stage pump can be comprehensively considered according to the area of the pump room, the pump price (the price of a multi-stage pump is generally higher than that of a single-stage pump) and other factors.
Type D & DG multistage pumps are used for feeding low and middle pressure
boiler water or for pumping other middle pressure water. The temperature of
pumped medium of type D are not more than 80°C and type DG 110°C.
Type D & DG pumps are horizontal single-suction centrifugal pump with ring
section body. The position of suction port of type D is arranged horizontal and that
of type DG is vertically up. The position of discharge port is arranged vertically up.
The shaft sealing of these pumps are sealed with soft-packing. At the location of
the shaft sealing, there is a renewable sleeve to protect the shaft.
The pumps are directly driven by the motor through the flexible coupling.
The rotating directions of the pumps are clockwise, when viewed pump from the
driving end