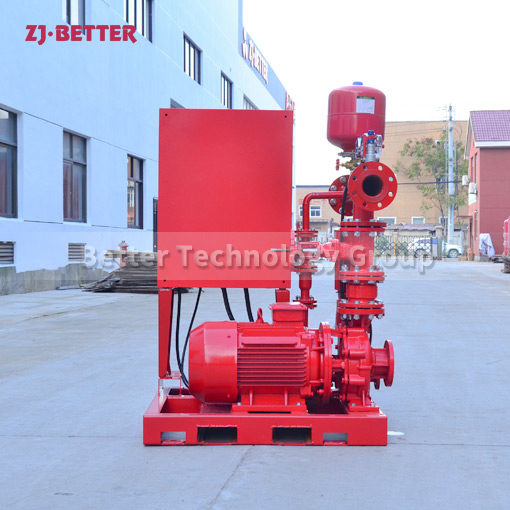
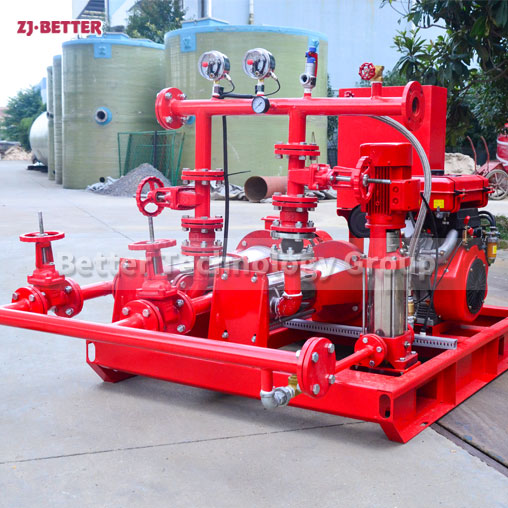
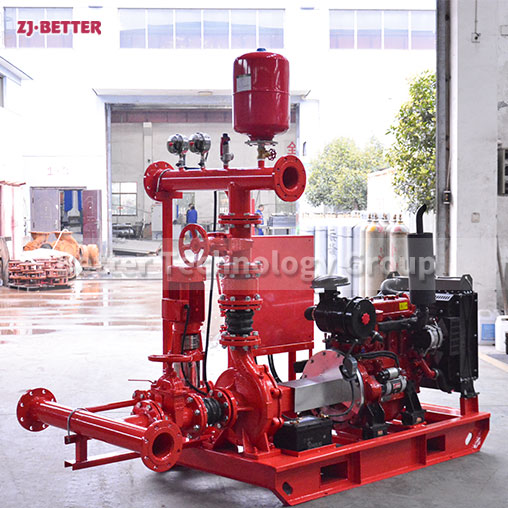
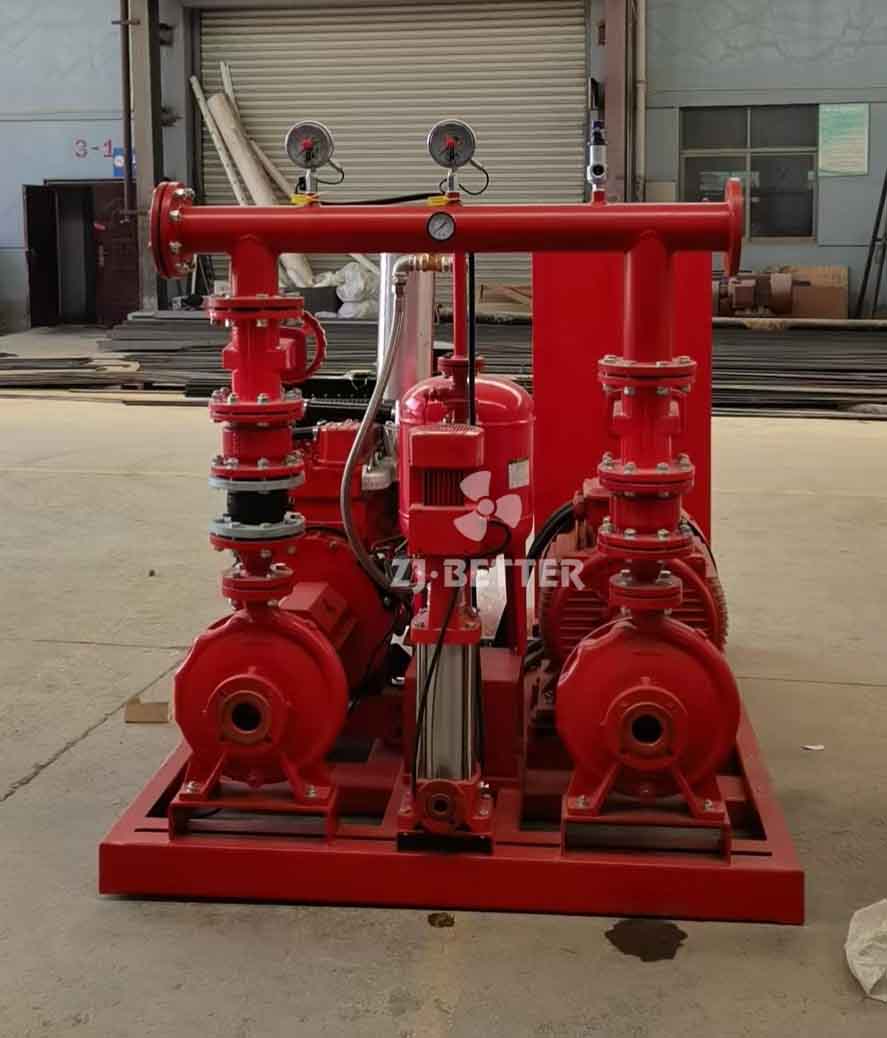
Fire pumps are classified into various types based on their specific applications and operational characteristics. The common classifications of fire pumps include:
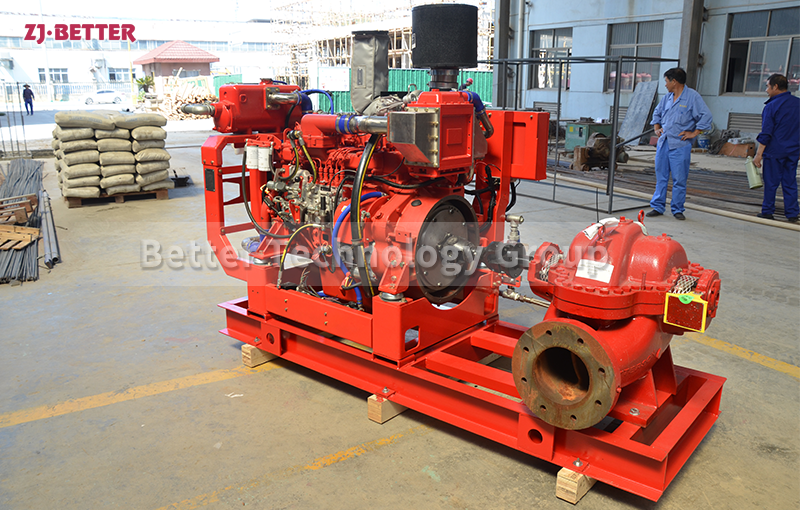
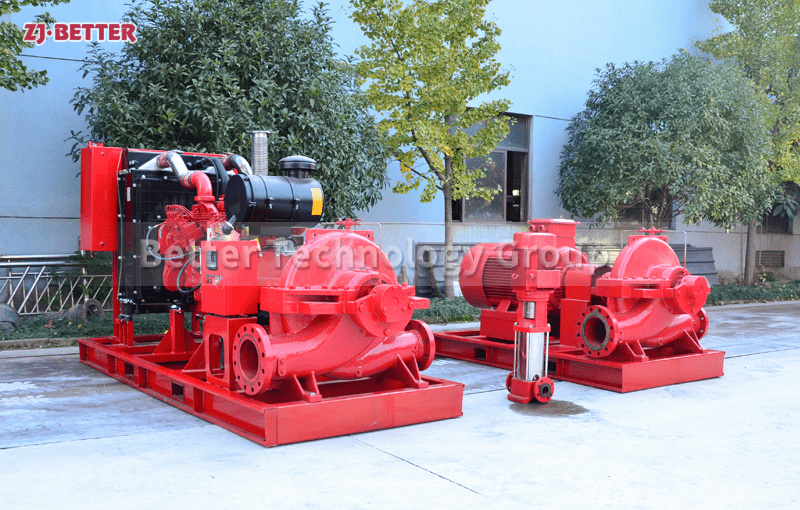
Horizontal Split Case Fire Pumps: These pumps have a horizontally split casing, which allows easy access to internal components for maintenance and repairs. They are typically used in large-scale fire protection systems, such as industrial facilities, commercial buildings, and high-rise structures. Horizontal split case pumps are known for their high flow rates and can handle a wide range of pressures.
Vertical Turbine Fire Pumps: Vertical turbine pumps have a vertical shaft and are designed to operate with submerged impellers. These pumps are commonly used in water sources such as wells, rivers, or lakes. Vertical turbine fire pumps are ideal for locations where space is limited, as they have a small footprint. They are also suitable for applications that require high pressures but lower flow rates.
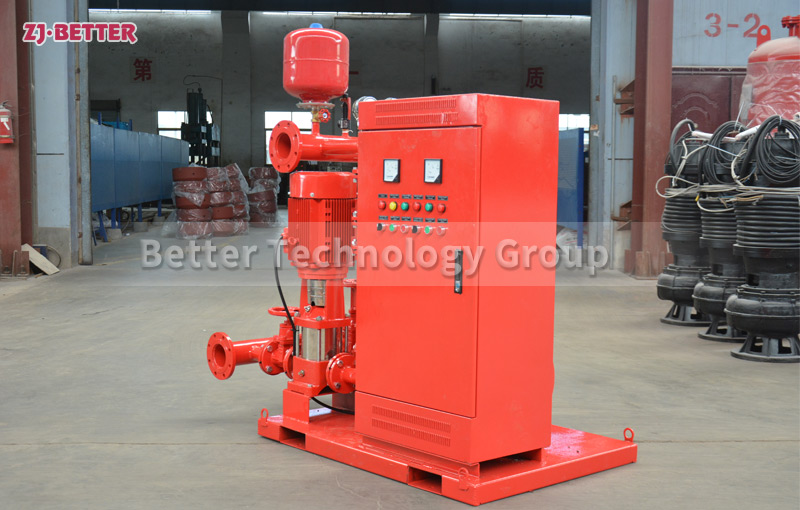
Vertical Inline Fire Pumps: Vertical inline pumps have a vertical design with the motor located above the impeller. These pumps are compact and space-saving, making them suitable for installations where floor space is limited. Vertical inline fire pumps are commonly used in commercial and industrial applications, such as office buildings, hospitals, and manufacturing facilities.
End Suction Fire Pumps: End suction pumps have a single impeller mounted on the end of the shaft. They are widely used in various applications, including fire protection systems. These pumps are known for their simplicity, ease of maintenance, and cost-effectiveness. End suction fire pumps are typically used in smaller buildings, residential properties, and light commercial applications.
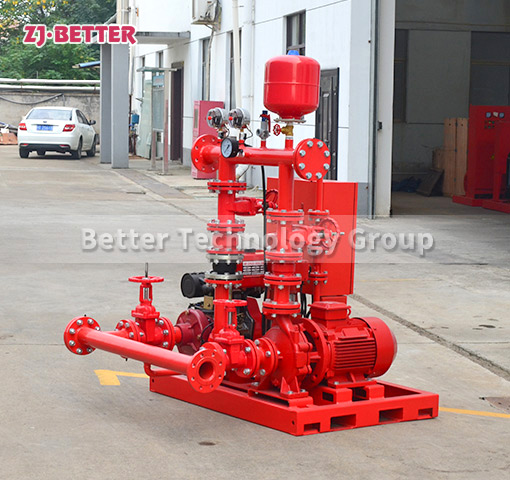
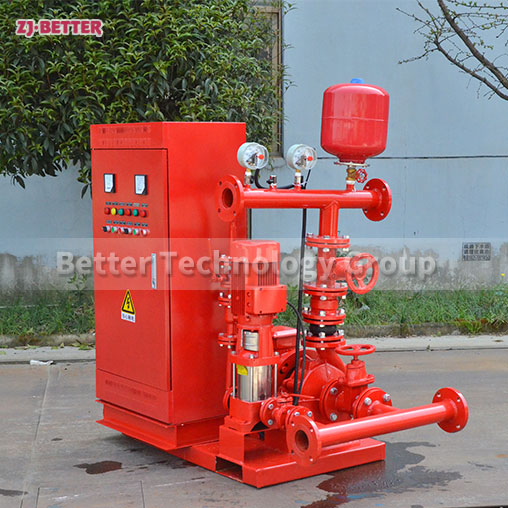
Multistage Fire Pumps: Multistage pumps consist of multiple impellers arranged in series. Each impeller adds pressure to the water, allowing these pumps to deliver high pressures. Multistage fire pumps are suitable for applications that require high-pressure delivery, such as high-rise buildings, industrial plants, and sprinkler systems with demanding pressure requirements.
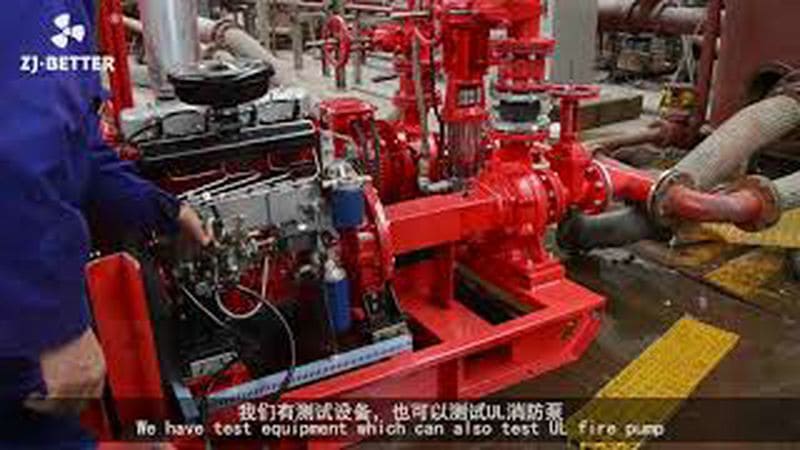
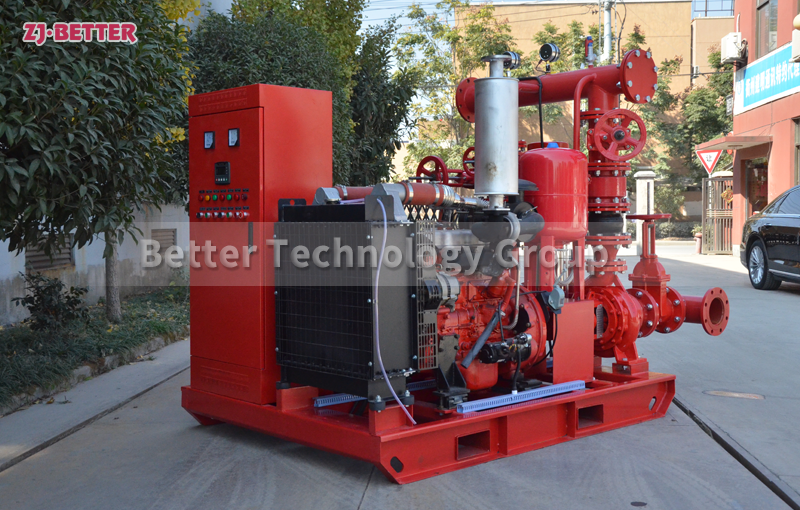
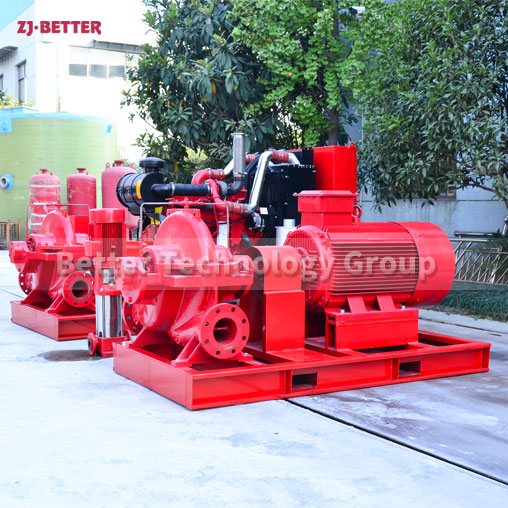
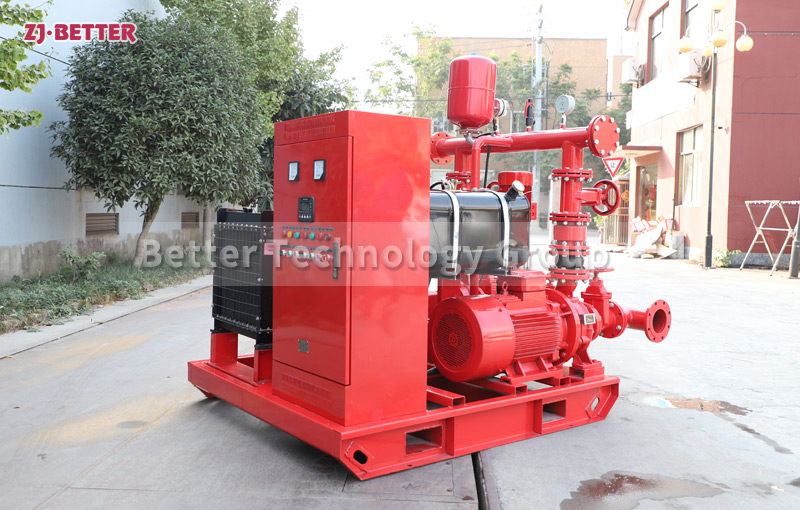
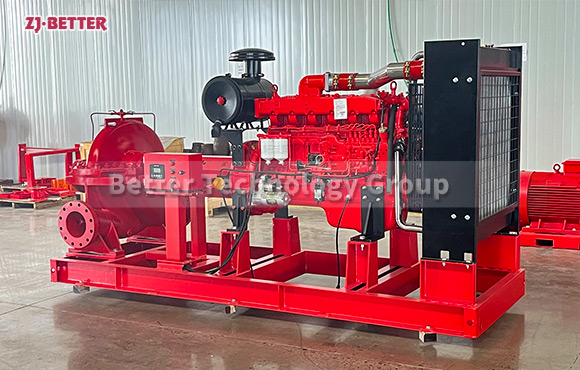
Diesel-Driven Fire Pumps: Diesel-driven fire pumps are powered by diesel engines, providing a reliable source of power in situations where electricity may be unavailable or unreliable. These pumps are commonly used in remote locations, off-grid areas, and critical infrastructure where continuous operation is essential. Diesel-driven fire pumps are known for their durability and ability to deliver high flow rates and pressures.
It’s important to note that these classifications are not exhaustive, and variations of fire pumps exist within each category. The choice of fire pump classification depends on factors such as system requirements, available space, flow rates, pressure requirements, and power sources. Consulting with fire protection experts or system designers can help determine the most suitable fire pump classification for a specific application.